Bone scintigraphy is an imaging test used most often to identify flashpoints caused by infections, arthritis, fracture, changes in bone blood circulation, evaluation of bone prostheses, or to investigate causes of bone pain, for example .
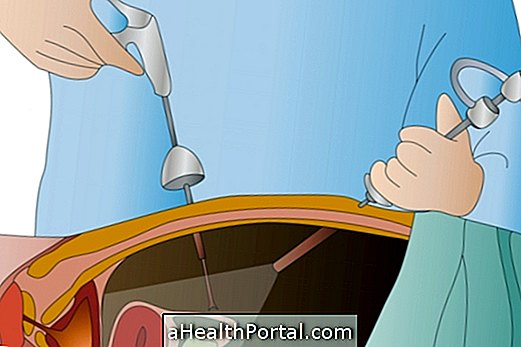
To perform this test, a radiopharmaceutical, such as the Technetium or Gallium, which is a radioactive substance, must be injected into the vein. These substances are attracted to the bone tissue with the disease after about 2 hours, which can be recorded using a special camera, which detects radioactivity and creates an image of the skeleton.
This examination is usually done in hospitals or nuclear medicine centers, which can be done free of charge by the SUS or in private centers, costing an average of R $ 500, 00 to 900, 00 reais, which is very variable according to the place where it is made. This examination is only done in necessary cases, with the proper medical indication.
How is it done?
Bone scintigraphy is started by injecting the radiopharmaceutical into the vein, which, although radioactive, is made in a safe dose for use in people. Next, the period of uptake of the substance through the bones should be waited, which takes about 2-4 hours, and it is possible to return home during this period, avoiding contact with pregnant women or babies, and drinking about 6-8 glasses of water to eliminate the rest of the radiopharmaceutical that has not accumulated in the bones.
After waiting, the patient should urinate to empty the bladder and lie down on the stretcher to begin the examination, done in a special camera that records the skeletal images on a computer. The sites where the radiopharmaceutical was most concentrated are highlighted, which means intense metabolic reaction in the region, as the image shows.
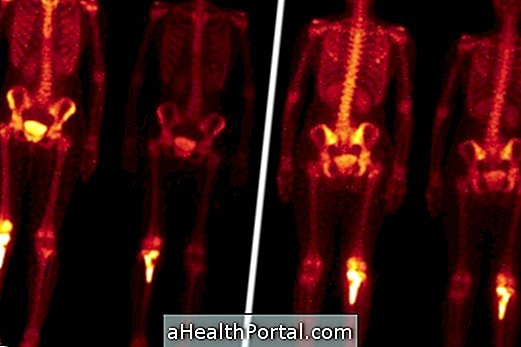
Bone scintigraphy can be performed for a specific region or whole body, and the examination usually lasts 30-40 minutes. The patient does not need to fast, or have any special care, or stop the medication. However, within 24 hours of the examination, the patient should not come in contact with pregnant women or infants, as they may be sensitive to the radiopharmaceutical that is eliminated during this period.
In addition, there is three-phase bone scintigraphy, when the images of the scintigraphy are to be evaluated in phases. Thus, in the first phase the blood flow in the bone structures is evaluated, in the second phase the blood balance in the bone structure is evaluated and, finally, the images of the radiopharmaceutical capture by the bones are evaluated.
What is it for
Bone scintigraphy may be indicated to identify in the following situations:
- Bone scintigraphy : search for bone metastases caused by various types of cancer, such as breast, prostate or lung, for example, and to identify areas of altered bone metabolism. Understand better what metastases are and when they happen;
- Three-phase bone scintigraphy : to identify alterations caused by osteomyelitis, arthritis, primary bone tumors, fractures, osteonecrosis, reflex sympathetic dystrophy, bone infarction, bone graft viability and evaluation of bone prostheses. It is also used to investigate causes of bone pain where the causes with other exams have not been identified.
This test is contraindicated for pregnant or breastfeeding women and should be done only after medical advice. In addition to bone scintigraphy, there are other types of scintigraphy performed on different organs of the body, to identify various diseases. Check out more in Scintigraphy.