Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of cancer in the blood that begins in the bone marrow and can spread to other parts of the body. This type of cancer has a greater chance of cure when it is diagnosed in its initial stage, when there are still no metastases and causes symptoms such as weight loss and swelling of the tumors and belly, for example.
Treatment of acute myeloid leukemia can be done at the cancer hospital and it is very intense in the first 2 months, and at least one more year of treatment is necessary for the disease to be cured.
This type of cancer of the blood proliferates very fast, and affects individuals of all ages, but is more frequent in adults, because the cancer cells accumulate in the bone marrow and are released into the bloodstream, where they are sent to other organs, such as liver, spleen or central nervous system, where they continue to grow and develop.
Symptoms of Acute Myeloid Leukemia
The most common symptoms of acute myeloid leukemia include:
- Anemia, which is less than normal amount of red blood cells;
- Feeling of weakness and general malaise;
- Pallor and headache that are caused by anemia;
- Frequent haemorrhages characterized by easy nose bleeding and increased menses;
- Occurrence of large bruises even in small strokes;
- Loss of appetite and weight loss without apparent cause;
- Swollen and painful tongues, especially in the neck and groin;
- Frequent infections;
- Pain in bones and joints;
- Fever;
- Shortness of breath and cough;
- Exaggerated night sweats, which gets to wet the clothes;
- Abdominal discomfort caused by swelling of the liver and spleen.
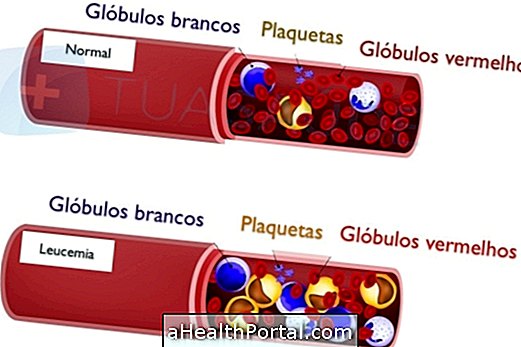
Acute myeloid leukemia is a type of blood cancer that most commonly affects adults and its diagnosis can be made after blood tests, lumbar puncture and bone marrow biopsy.
The diagnosis can be made through a blood test, as a blood count that allows you to observe the decrease of white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets, but to confirm the diagnosis a biopsy of the bone marrow is necessary. To learn more about the blood tests read: Check out the blood tests that detect the cancer.
Classification of acute myeloid leukemia
Myeloid leukemia is classified into several subtypes, as shown below:
| Types of Myeloid Leukemia | Prognosis of the disease |
M0 - Undifferentiated Leukemia | Too bad |
| M1 - Acute myeloid leukemia without differentiation | Medium |
| M2 - Acute myeloid leukemia with differentiation | Good |
| M3 - Promyelocytic Leukemia | Medium |
| M4 - Myelomonocytic Leukemia | Good |
| M5 - Monocytic Leukemia | Medium |
| M6 - Erythroleukemia | Too bad |
M7 - Megakaryocytic Leukemia | Too bad |
The chances of cure of acute myeloid leukemia vary according to the type of leukemia, when the diagnosis was made and the state of health of the patient.
Treatment for acute myeloid leukemia
Treatment for acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) is indicated by the oncologist and can be performed through multi-drug chemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation.
Chemotherapy may include taking medications such as cytarabine for 1 week and daunorubicin for 3 days, and even thioguanine or vincristine and prednisone, for example. This treatment decreases the amount of white blood cells in the body, and leaves the patient vulnerable to infections, and symptoms such as fatigue, fatigue and anemia and if there is infection your treatment should be done with antibiotics.
A few months after the initial treatment, the patient undergoes additional chemotherapy, which ensures the elimination of as many cancer cells as possible. See more details on treatment in: Treatment for Acute Myeloid Leukemia.