The bubonic plague, commonly known as the Black Plague, is a serious and often fatal disease caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis, which is transmitted through the fleas of rodent animals to humans.
This plague had a very important outbreak in the Middle Ages, killing nearly 30% of the population of Europe, but today it is quite rare, being more frequent in some places of sub-Saharan Africa and in the islands of Madagascar, for example. In Brazil, the last reported cases were after the year 2000, with only two cases in the whole country, in Bahia and Ceará.
When black plague is suspected, it is very important to seek medical help as soon as possible, as people who do not receive the treatment within 48 hours are at high risk for life.
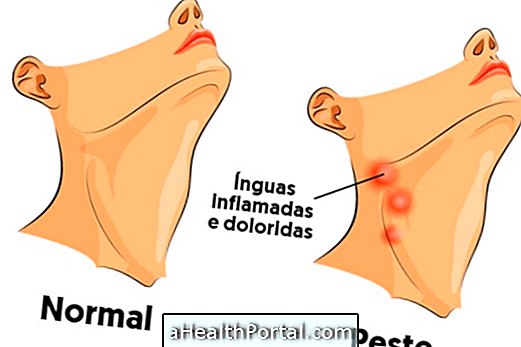
Main symptoms
There are 3 main types of plague, which vary according to how the disease was transmitted and the symptoms presented:
1. Bubonic plague
It is the best-known type of plague that causes symptoms such as:
- Fever above 38º C;
- Constant shivers;
- Severe headache;
- Excessive tiredness;
- Tongues very swollen and sore.
Enews usually become inflamed near the flea bite site, but if the treatment has not started, the infection can spread throughout the lymphatic system, affecting the whole body.
2. Septicemic plague
In this type of plague, in addition to excessive tiredness, fever and chills, other signs may also appear, such as severe abdominal pain and purple spots on the skin caused by bleeding under the skin. In addition, some skin sites may become black due to tissue death, which is more common in the nose and fingers and toes.
3. Pneumonic plague
This pest is accompanied by the development of pneumonia, so some common signs include difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, chest pain, and constant coughing that in some cases may include the presence of blood.
Bubonic plague can arise from the inhalation of particles contaminated by rat feces, but it is also a common complication of other types of plague, especially when treatment is not started.
How is the diagnosis made?
Typically, the diagnosis of plague is suspected when it has been in places with cases of the disease and typical symptoms appear, such as swelling of the throat, fever and excessive tiredness.
However, it is possible to confirm the diagnosis by blood examination or biopsy of a piece of tissue removed from an eye, for example.
How transmission can happen
The transmission of bubonic plague is done through rodents, especially rats, but usually the disease reaches humans through the flea. This happens because after causing death to the mouse, the flea usually migrates to other bodies to continue feeding on the blood.
After biting the human skin, the flea bacteria settle into the nearest lymph node and multiply there, generating all plague-related symptoms.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for any type of plague should be done with the use of antibiotics such as gentamicin, streptomycin, tetracycline or doxycyclin for 10 days in a row. During the treatment you need to be hospitalized in an isolation room to avoid passing the disease on to others.
Ideally, treatment should be started as soon as the first symptoms begin, to ensure success. Thus, if the disease is suspected, it is very important to go to the hospital quickly to confirm the diagnosis and to start using the antibiotic.