The dangers of inhaling fire smoke vary from burns in the airways such as the development of respiratory diseases such as bronchiolitis and pneumonia up to 5 days after the incident. This is because carbon monoxide is a toxic substance that generates accumulation of blood and liquids in the region, preventing the passage of air.
Depending on the amount of smoke that has been inhaled, the individual may evolve from respiratory intoxication to death within 2 to 5 minutes. However, individuals who inhaled a smaller amount of smoke can still suffer their consequences for up to 3 weeks by developing respiratory infections.

Situations caused by inhalation of fire smoke
The main situations caused by the inhalation of smoke from fires are:
- Burning in the respiratory tract: The heat from the flames causes burns inside the nose, larynx and pharynx. This type of burn leads to swelling of the airways preventing the passage of air. It is enough that the person is exposed to smoke from the fire for about 10 minutes to have their airways burned.
- Choking / lack of oxygen: Fire consumes the oxygen present in the air and so breathing becomes increasingly difficult. With this there is accumulation of CO2 in the blood and with less oxygen reaching the lungs the person feels weak, becomes disoriented and faints. If she is not rescued, in less than 10 minutes she may not survive. The longer you go without oxygen, the greater the risk of death or brain damage and permanent neurological sequelae.
- Poisoning by toxic substances in the smoke: The smoke of a fire contains several different particles, and among them are chlorine, cyanide and sulfur, which cause airway swelling, extravasation of fluid and consequently prevent the passage of air through the lungs .
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Inflammation and accumulation of fluid inside the airways may prevent the passage of air. Both the heat of the smoke and the toxic substances present in it can lead to the development of pulmonary edema which is when there is an accumulation of fluid and blood that forms inside the lungs, preventing the exchange of oxygen.
- Pneumonia: With the affected respiratory system there is greater ease of entry and proliferation of viruses, fungi or bacteria can lead to the development of pneumonia. This may manifest up to 3 weeks after the incident.
Most surviving victims of a fire recover completely having no breathing problems in the future, but victims who inhaled a large amount of toxic smoke may experience difficulty breathing, dry cough and hoarseness for months.
Warning Signs
The main warning signs that can arise in the victims of a fire include:
- Cough; wheezing;
- Fever; difficulty breathing;
- Dizziness, feeling sick, fainting,
- Mouth and bluish or bluish fingertips.
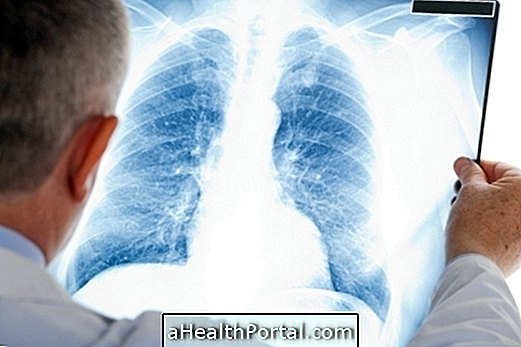
When you notice any of these symptoms you should seek a doctor, without taking any medication, to avoid that it masters the symptoms and makes difficult the diagnosis of the disease. The individual should be observed, the doctor may order tests such as chest x-ray and arterial blood gases, and the individual may be admitted to the ICU Intensive Care Unit until he or she is fully recovered.
Anyone who has been exposed to smoke from a fire for more than 10 minutes needs to be observed at the hospital for 24 hours because signs of respiratory infection may take hours to start manifesting.
If there are no signs or symptoms, doctors may be discharged but still recommend that if any symptoms are present within the next 5 days, the person should return to the hospital for appropriate treatment.
How treatment for fire victims is done
Treatment should be done at the hospital and can be done with the use of wet towels in saline and ointments to protect burned skin, but respiratory care is essential to ensure the safety of the victim.
All victims need 100% oxygen masks to be able to breathe better. Doctors can observe the signs of respiratory distress and evaluate the passage of air through the nose, mouth and throat, assessing the need to put a tube into the mouth or neck of the victim so that she can breathe even with the help of appliances.
Within 4 to 5 days the burned tissues of the airways should begin to loosen, along with some secretion, and at this stage the person may need aspiration of the airways so as not to suffocate with the waste tissues.