Gonorrhea in pregnancy can bring major complications to the baby, including usually eye injuries, blindness, and generalized infection if the disease is transmitted at delivery. If the mother with gonorrhea detects the symptoms early, she can make a treatment based on antibiotics, avoiding greater consequences to the baby.
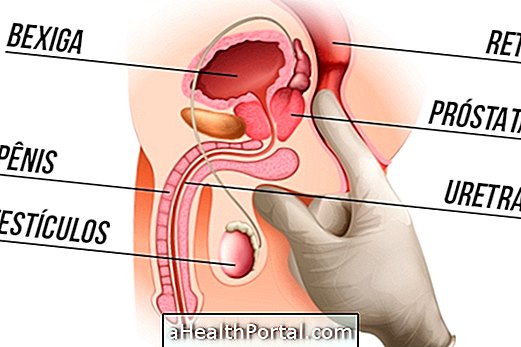
Gonorrhea is an infection caused by the highly contagious sexually transmitted Neisseria gonorrhoea bacterium. It usually affects the cervix, but may be present in the urethra, rectum, or throat. It can be asymptomatic or cause vaginal discharge, pain and urinary discomfort.
Is gonorrhea in pregnancy dangerous for the baby?
Gonorrhea in pregnancy is dangerous for the baby, especially if the birth is due to normal delivery, as the child may be contaminated by the bacterium present in the genital area of the infected mother, at risk of causing neonatal conjunctivitis and, sometimes, blindness and infection, requiring intensive treatment.
During pregnancy, although the likelihood of the baby being infected is lower, gonorrhea is associated with increased risk of miscarriage, amniotic fluid infection, premature birth, premature rupture of membranes, and fetal death.
Gonorrhea is also one of the major causes of pelvic inflammation, which damages the fallopian tubes, leading to ectopic pregnancy and sterility. In postpartum there is an increased risk of pelvic inflammatory disease and spread of infection with joint pain and skin lesions.
Treatment for Gonorrhea in Pregnancy
The treatment for gonorrhea in pregnancy is the use of antibiotics for a period of time that varies according to the type and severity of the infection. Typically, gonorrhea, if detected early, is limited to the genital region and the most effective treatment is through the use of a single dose of antibiotic.
Some treatment options for gonorrhea are the following antibiotics:
- Penicillin;
- Ofloxacin 400 mg;
- Granulated Tianfenicol 2.5 g;
- Ciprofloxacin 500 mg;
- Ceftriaxone 250 mg intramuscular;
- Cefotaxime1 g;
- Spectinomycin 2 mg.
In view of the complications that gonorrhea can cause to the woman and the baby, it is important that the partner is also treated, avoiding sexual relations while the disease is not resolved, maintaining a single sexual partner, using condoms and always following all the guidelines during pregnancy.
Useful links:
- Gonorrhea has a cure
- Home remedy for gonorrhea