Most often, changes in the eye are not a sign of a serious problem, being more frequent due to fatigue or a slight irritation of its coating, caused by dry air or dust, for example. This type of alterations last about 1 to 2 days and disappear by itself, without needing treatment.
However, when changes occur that last more than 1 week or cause any discomfort, they may indicate the presence of a health problem such as infection or liver problems. In these cases, it is advisable to consult an ophthalmologist to identify if there is any disease that needs to be treated.
1. Red eyes
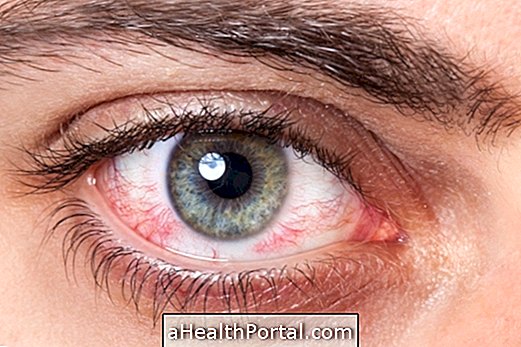
In most cases, red eyes are caused by eye irritation, which can happen due to too dry air, dust, wear of lenses and even minor nail trauma, for example. This type of change causes only a slight burning sensation and can sometimes present only a small red spot on the white of the eye, which disappears by itself in a few minutes or hours, requiring no specific treatment.
See in this video the main causes of red eyes:

However, when other signs such as intense itching, excessive tearing or sensitivity to light appear, red eye may also be a sign of allergy or infection and it is advised to consult an ophthalmologist to start the appropriate treatment. Know when it may be an eye infection.
2. Tremendous eyes
The trembling eye is usually a sign of tiredness and is therefore very common when you are standing in front of your computer or straining your eyes. Usually, the problem causes a slight tremor that goes back and forth and can last up to 2 or 3 days.
However, when the tremor is more frequent and lasts more than 1 week to disappear, it can also indicate other problems such as lack of vitamins, vision problems or dry eye. See in what situations the tremendous eye can indicate health problems.
3. Yellow eyes

The presence of yellowing of the eyes is usually a sign of jaundice, a change that occurs due to the accumulation of bilirubin in the blood, which is a substance produced by the liver. So when this happens, it is very common to suspect some disease or inflammation in the liver, such as hepatitis, cirrhosis or even cancer.
This type of problem is more common in older people or those who eat an unbalanced diet and drink alcohol often, for example. Thus, if yellow eyes appear, one should go to a hepatologist to do liver exams and identify the specific problem by initiating treatment. See the 11 symptoms that may help confirm a problem with this organ.
4. Outgoing eyes

The bulging and bulging eyes are usually a sign of Graves' disease, which causes increased thyroid function, also known as hyperthyroidism.
In these cases, other symptoms such as palpitations, excessive sweating, easy weight loss or constant nervousness are also common, for example. So if this eye change arises it is advisable to take a blood test to evaluate the amount of thyroid hormones. Get to know other signs that can help identify Graves' disease.
5. Eyes with gray ring

Some people may develop a gray ring around the cornea, where the color of the eye joins with the white. This is usually due to triglycerides or high cholesterol, which may indicate an increased risk of cardiovascular problems such as heart attack or stroke.
People with this change should go to the general practitioner and ask for a blood test to check their cholesterol levels, especially if they are under age 60. Typically, high cholesterol can be treated with dietary changes, but medications may also be prescribed. Learn more about how this issue is handled:

6. Eye with white cloud

The presence of a white cloud in the eye is more common in the elderly due to the onset of cataracts, which are caused by the lensing of the lens of the eye that happens naturally with aging. However, when they appear in young people, it can indicate other diseases like decompensated diabetes or, even, tumor.
Normally, cataracts can be treated with surgery, so it is important to see an ophthalmologist. In other cases, it is important to consult a general practitioner to find out if there is another cause and start the appropriate treatment.
7. Drooping eyelids

When the eyelids are drooping in both eyes, they may indicate the presence of myasthenia gravis, an autoimmune disease that causes progressive weakness of the muscles, especially in women in their 20s and 40s. Normally, weakness appears in the smaller muscles such as the eyelids, but may end up affecting the head, arms and legs.
Thus, people with this disease may also begin to present other symptoms such as keeping their heads hanging, having difficulty climbing stairs or weakness in their arms. Although it has no cure, treatment helps improve the quality of life. Understand more about the disease how the treatment is done.