Treatment for eye injuries and strokes depends on the type and severity of the injury and may require only a home treatment with water or artificial tears for less serious accidents or use of antibiotics and other medications in the most severe cases.
Eye accidents are common at any stage of life, and it is important to remember what caused the accident and how long ago the wound or irritation symptoms were identified.
Here's what to do in each case.
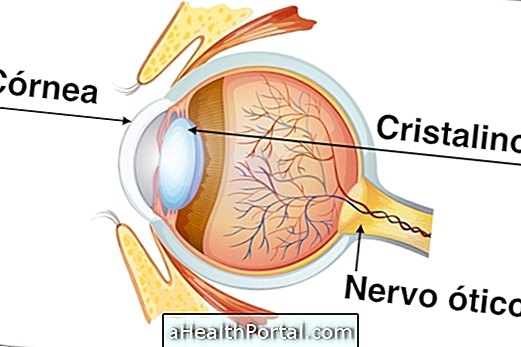
Scratch on the cornea - dust or nails
Also called abrasion on the cornea, the scratch is usually caused by nails, dust, sand, sawdust, loose metal particles or the tip of a sheet of paper.
In general, simple scratches heal naturally within up to 2 days, but if symptoms of pain, sand in the eye, blurred vision, headache and watery eyes appear, seek medical help. In these cases it is appropriate to wash the eye only with clean running water and blink the eye several times to help eliminate the foreign body.
In addition, to avoid complications until reaching the doctor, avoid rubbing or scratching the eye and do not try to remove the foreign body, especially using objects such as nails, swab or tweezers, as this may aggravate the eye injury. See more tips here.

Penetrating wound - Pointed objects or punches
They are wounds that pierce the eye, being caused mainly by sharp objects like pencils, tweezers or kitchen utensils, or by blows or punches.
This type of injury causes ocular swelling and bleeding, and if the object is dirty or contaminated with microorganisms, it can lead to an infection that spreads throughout the body.
Thus, treatment should always be done with the doctor, and only cover the eye with gauze or clean cloth before going to the emergency room to start treatment quickly.
Cuts in the eyes or eyelids
They are also caused by sharp or sharp objects such as knives, pencils and scissors, and the patient should be taken immediately to the emergency room.
Depending on the type of cutting object and the severity of the injury, stitches or antibiotics may be needed to fight infections.
Bleeding
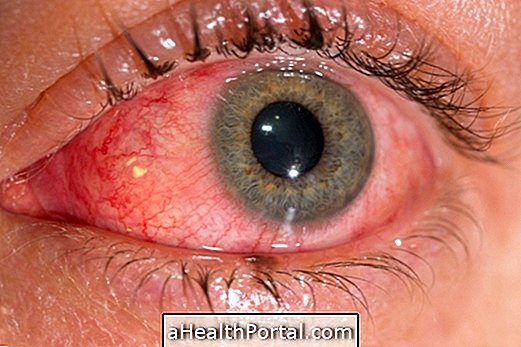
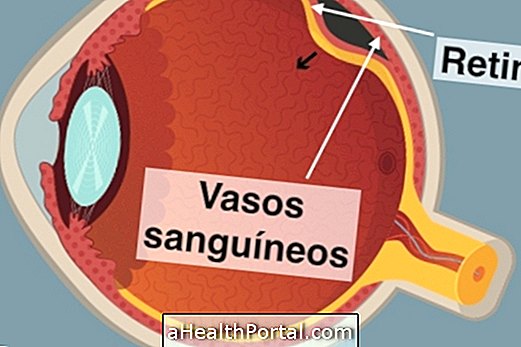
Bleeding may be due to wounds and cuts in the eyes, and should always be evaluated by the physician to identify complications such as perforations, rupture of the eyeball or detachment of the retina, which may cause decreased vision or blindness.
In general, bleeding stops within 1 week, and it is necessary to stop using medications such as aspirin and anti-inflammatories as they may stimulate ocular hemorrhage.
Heat burns or weld sparks
In cases of heat burn, such as contact with hot objects, one should only wash the eye and eyelids with running cold water and place a damp cloth over the eye regularly until reaching the first aid to keep the area moist. However, dressings should not be done as they can cause wounds and ulcers on the cornea.
Even in cases of burns without the protection of the glasses, the symptoms of the damaged eye, such as sensitivity to light, pain, redness and tearing, may take up to 12 hours to appear. As soon as these symptoms appear, the doctor should be sought to start the appropriate treatment.
Chemical Burns
They can be caused by the use of chemicals at work, by car battery blasts or by cleaning products at home, for example, and they need urgent first aid care.
Therefore, the victim should wash the eye with tap water for at least 15 minutes, preferably lying down or sitting with his head turned back.
Upon reaching the emergency room, the doctor will assess whether the cornea has been affected and may indicate the use of antibiotic tablets or drops and drops of vitamin C to put into the eyes.
See other eye care:
- Causes and Treatments for Redness in the Eyes
- Simple Strategies to Fight Eye Pain and Tired Vista
- Understand why it is possible to have one eye of each color