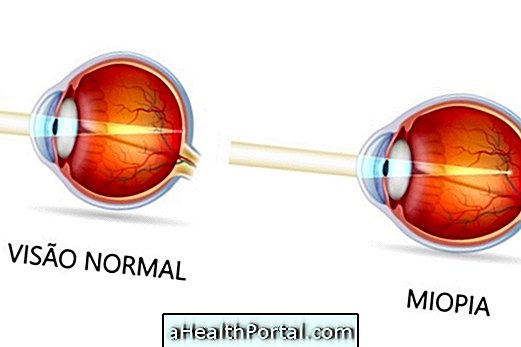
When diabetes is not adequately controlled, with care in food or with the intake of drugs prescribed by the endocrinologist, blood sugar levels can be elevated for a long time, causing progressive damage to the retina and blood vessels of the eyes, leading to blurred vision, difficulty seeing, and, in more advanced cases, blindness. See all you can do to control your sugar levels.
In addition, these changes in vision, scientifically known as diabetic retinopathy, can be aggravated when you have another disease such as hypertension, kidney problems or high cholesterol, for example.
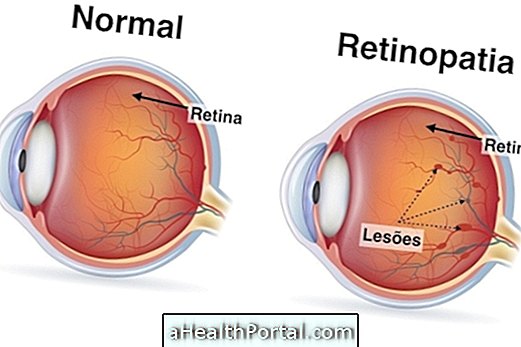
Diabetic retinopathy can be divided into 2 different types:
- Nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy: it is the least severe type of problem that presents only minor lesions in the blood vessels of the eye;
- Proliferative diabetic retinopathy: it is the most severe type that causes the appearance of more fragile vessels in the eye, which can rupture, worsening vision or causing blindness.
This change in vision caused by diabetes has no cure, but its evolution and aggravation can be avoided with the use of some treatments recommended by the ophthalmologist, such as laser or conventional surgery.
What are the most common symptoms
The main symptoms of diabetic retinopathy include:
- Small black spots or lines in the view;
- Blurry vision;
- Dark spots on vision;
- Difficulty in seeing;
- Difficulty identifying different colors
However, these symptoms are not always easy to identify before the onset of blindness, so it is very important that people with diabetes keep their blood sugar levels well controlled and have regular visits to the eye doctor to assess their eye health.
Treatment options available
The treatment should always be directed by an ophthalmologist and usually varies according to the severity and type of retinopathy of the patient, and in cases of non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy the doctor can only choose to monitor the evolution of the problem without doing any type of treatment.
In cases of proliferative diabetic retinopathy, it is usually necessary to have surgery or laser treatments to eliminate the new blood vessels that are forming in the eye or to stop a bleeding if it is happening.
However, the patient should always maintain adequate diabetes treatment to avoid worsening of retinopathy, even in cases of non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
In addition to retinopathy, diabetes can also cause other complications such as diabetic foot, see how to protect yourself from the complications of diabetes.