Exophthalmos, also known as ocular proptosis or bulging eyes is a medical condition in which one or both eyes of a person are more prominent than normal, which can be caused by an inflammatory process or some problem that leads to the narrowing of the eye. orbital cavity.
There are several causes that may be at the origin of this problem, such as thyroid disease, infections in the orbital cavity, among others. The treatment depends on the cause that causes the exophthalmos, and can be performed with antibiotics, anti-inflammatories, surgery and in the case of a tumor, radiotherapy or chemotherapy.
Exophthalmos may be unilateral, when the protrusion of the eyeball occurs only on one side, or bilaterally, when both eyes are protruding.

What causes
The most common causes of exophthalmos are:
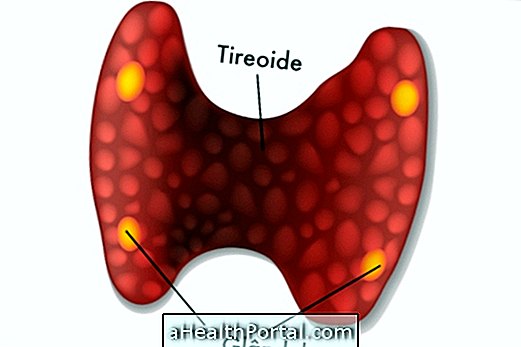
1. Graves Disease
One of the major causes of exophthalmos is Graves' disease. This is an autoimmune disease, in which the body's antibodies attack the thyroid, causing hyperthyroidism and leading to the occurrence of various symptoms, including orbital inflammation. Learn more about Graves' disease.
How to treat
The treatment for exophthalmos caused by Graves' disease consists of administration of 60 mg a day of oral prednisone for one month, followed by decreasing doses over several months. In addition, optical lubricants, eyelid surgery, ocular musculature surgery, or orbital decompression may also be used.
2. Orbital cellulitis
Cellulitis in the eye is caused by a bacterial infection by bacteria that colonize the skin after an injury or that spread from a nearby infection such as a sinusitis, conjunctivitis or a dental abscess, for example, causing symptoms like pain, swelling, difficulty moving the eye or exophthalmos. Learn more about cellulitis in the eye.
How to treat
The treatment consists of the administration of antibiotics and in more severe cases it may be necessary to resort to surgical drainage of the orbital abscess.
3. Tumors
Tumors of the orbit cause progressive and painless exophthalmos, the most common being hemangioma, lymphangioma, neurofibroma, dermoid cyst, adenoid cystic carcinoma, optic nerve glioma, optic nerve meningioma, and benign mixed tumor of the lacrimal gland.
How to treat
If a timely diagnosis is made by fine needle puncture followed by urgent radiotherapy, it may be possible to preserve vision.
4. Carotid-cavernous fistulas
Carotid-cavernous fistulas are abnormal communications between the carotid arterial system and the cavernous sinus, which is characterized by an arterial blood flow from a high pressure system of the internal or external carotid artery to the low pressure venous system of the cavernous sinus . These fistulas, draining through the orbit can cause exophthalmos, double vision and glaucoma.
How to treat
The treatment consists of an intravascular embolization.