Cancer is one of the most serious diseases due to its ability to spread cancer cells throughout the body, affecting nearby organs and tissues, but also more distant locations. These cancer cells that reach the other organs are known as metastases.
Although the metastases are in another organ, they continue to be formed by cancer cells from the initial tumor and, therefore, it does not mean that cancer has developed in the new affected organ. For example, when breast cancer causes metastasis in the lung, the cells remain the breast and must be treated in the same way as breast cancer.

Metastasis symptoms
In most cases, metastases do not cause new symptoms, however, when they do occur, these symptoms vary depending on the affected site, including:
- Bone pain or frequent fractures, if it affects the bones;
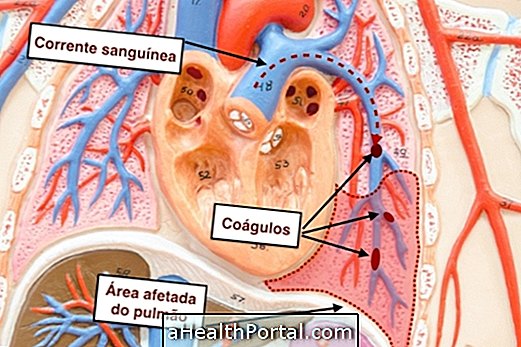
- Difficulty breathing or feeling short of breath, in the case of lung metastases;
- Severe and constant headache, convulsions or frequent dizziness, in the case of brain metastases;
- Yellow skin and eyes or swelling of the belly if it affects the liver.
However, some of these symptoms may also arise due to cancer treatment, and it is advisable to inform the oncologist of all new symptoms, so that the possibility of being related to the development of metastases is evaluated.
Metastases are indicative of malignant neoplasms, that is, that the organism was not able to fight the abnormal cell, favoring the abnormal and uncontrolled proliferation of malignant cells. Understand more about malignancy.
As it happens
Metastasis happens due to the low efficiency of the organism with regard to the elimination of abnormal cells. Thus, malignant cells begin to proliferate in an autonomous and uncontrolled manner, being able to pass through the walls of the lymph nodes and blood vessels, being transported by the circulatory and lymphatic system to other organs, which may be close to or distant from the primary site of the tumor.
In the new organ, cancer cells accumulate until they form a tumor similar to the original. When they are in large numbers, the cells are able to cause the body to form new blood vessels to bring more blood to the tumor, favoring the proliferation of more malignant cells and, consequently, their growth.
Main sites of metastasis
Although metastases can appear anywhere on the body, the areas that are most often affected are the lungs, liver and bones. However, these locations may vary according to the original cancer:
Can metastasis be cured?
When the cancer spreads to other organs, it is more difficult to reach a cure, however, the treatment of metastases must be kept similar to the treatment of the original cancer, with chemotherapy or radiotherapy, for example.
The cure is difficult to be achieved because the disease is already at a more advanced stage, and the presence of cancer cells in various parts of the body can be observed.
In the most severe cases, in which the cancer is very developed, it may not be possible to eliminate all metastases and, therefore, the treatment is done mainly to relieve the symptoms and delay the development of the cancer. Understand how cancer treatment is done.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther