An ointment developed at the laboratories of the Federal University of Alagoas by 4 teachers may be one more weapon against HPV. The ointment is prepared with a medicinal plant called Barbatimão, scientific name Abarema cochliocarpos, very common in the Brazilian northeast.
According to studies conducted this ointment may be able to eliminate the warts when applied twice a day in the region, and apparently there are no side effects related to its use. In addition, it is believed that it can completely eliminate the virus, avoiding the reappearance of genital warts because it acts by dehydrating the cells affected by the virus, until they dry, peel and disappear.
However, this ointment has been tested in only 46 people, so further studies are needed to confirm that barbatimon is actually effective in eliminating the virus. After this step it is also necessary to obtain the approval of ANVISA, which is the body responsible for regulating the sale of medicines in the national territory until this ointment can be purchased in pharmacies, under medical supervision.
Understand What HPV Is
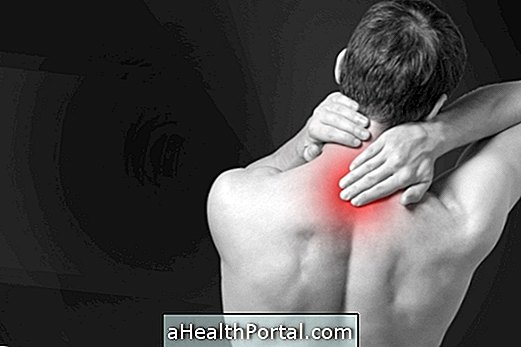
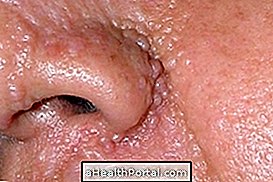
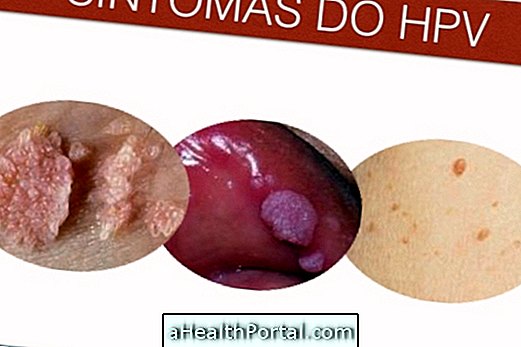
HPV, also known as human papillomavirus, is an infection that can cause the appearance of warts on the skin. Usually, the warts appear in the genital region of the man or woman, but can also affect other parts of the body, such as anus, nose, throat or mouth. These warts can also lead to the development of cervical, anus, penis, mouth or throat cancer.
How is the treatment done?
HPV treatment usually includes the removal of the warts through:
- Application of creams or acids such as Imiquimod or Podofilox, for example, that strengthen the immune system and help remove the outer layers of the warts until they disappear;
- Cryotherapy: consists in freezing the warts with liquid nitrogen until they disappear in a few days;
- Electrocauterization: an electric current is used to burn the warts;
- Surgery: A minor surgery is done at the doctor's office to remove the warts with scalpel or laser.
However, as there are no remedies capable of eliminating the virus being recommended strengthen the body with medicines prescribed by the doctor, such as Interferon, or with the intake of vitamin C either through supplements or through fruits such as orange, kiwi. See treatment details by clicking here.
Transmission and prevention
Transmission most often occurs through unprotected intimate contact, and therefore HPV is considered the most common sexually transmitted disease. However, it can also be transmitted through direct contact with HPV warts, as in the case of the normal birth of a pregnant woman with genital warts.
To prevent the transmission of this disease, there is a vaccine against HPV that can be taken by girls aged 9 to 45 and boys between 9 and 26 years old and which reduces the risk of being infected. However, condom use is best prevented during intimate contact, even after taking the vaccine.
Here's how to identify and treat HPV by watching the video below: