The chances of surviving an aneurysm vary depending on your size, location, age, and overall health. However, in most cases it is possible to live for more than 10 years with an aneurysm, without ever presenting any symptoms or having any complications.
In addition, many cases can be operated upon diagnosis, to remove the aneurysm or to strengthen the walls of the affected blood vessel, reducing, almost completely, the chances of rupture. However, the diagnosis is very difficult and, therefore, many people only know when the rupture occurs or when they do a routine examination that ends up identifying the aneurysm.
Here are some signs that may indicate the presence of an aneurysm.
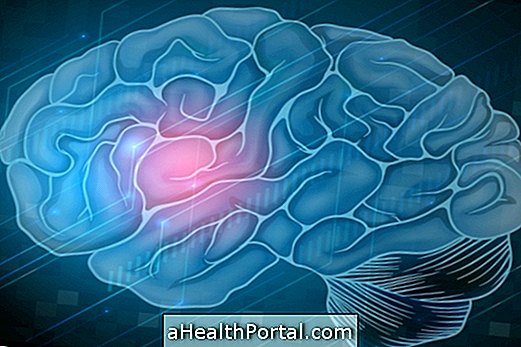
Symptoms of ruptured aneurysm
Symptoms of rupturing an aneurysm vary depending on your location. The two most common types are the aortic aneurysm and the cerebral aneurysm, and in these cases the symptoms include:
Aortic aneurysm
- Sudden severe pain in the belly or back;
- Pain radiating from the chest to the neck, jaw or arms;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Feeling of fainting;
- Paleness and purplish lips.
Brain aneurysm
- Severe headache;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Blurry vision;
- Severe pain behind the eyes;
- Difficulty walking;
- Weakness and dizziness;
- Drooping eyelids.
If there is more of these symptoms, or if an aneurysm is suspected, it is very important to go immediately to the emergency room or call for medical help by calling 192. The aneurysm is an emergency situation and therefore the more early treatment is started, the chances of survival are greater and the risk of sequelae is lower.
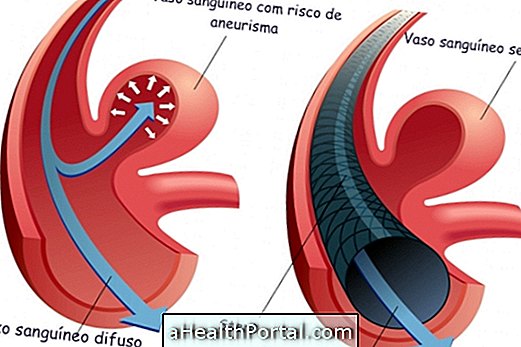
When there is a greater chance of rupture
The risk of a rupturing aneurysm increases with aging, especially after age 50, because the walls of the arteries become more fragile and so may end up breaking with blood pressure. In addition, people who smoke, who drink lots of alcohol or suffer from uncontrolled high blood pressure also have a higher risk of breakage.
Regarding the size of the aneurysm, in the case of the cerebral aneurysm, the risk is greater when it is more than 7 mm or when it is more than 5 cm in the case of the abdominal or aortic aneurysm. In such cases, treatment with surgery for correction of the aneurysm is usually indicated, after evaluation of the risk by the physician. Understand how the treatment is done in the case of cerebral aneurysm and aortic aneurysm.
Can Pregnancy Increase the Risk of Breaking Up?
Although the woman's body undergoes several changes during gestation, there is no increased risk of rupturing aneurysms, even during delivery. However, many obstetricians prefer to opt for cesarean section to lessen the stress caused by natural delivery on the body, especially if the aneurysm is too large or if a previous rupture has already occurred.
Possible sequels of aneurysm rupture
The major complication of aneurysm rupture is the risk of death, as internal bleeding caused by rupture may be difficult to stop, even with adequate treatment.
However, if it is possible to stop bleeding, there is still the possibility of other sequelae, especially in the case of cerebral aneurysm, since the bleeding pressure can cause brain damage, resulting in complications similar to a stroke, such as muscle weakness, difficulty to move a part of the body, loss of memory or difficulty speaking, for example. See a list of other bleeding sequels in the brain.