The brain tumor is characterized by the presence and proliferation of abnormal cells in the brain or meninges, which can happen due to genetic mutations or due to cancer metastasis from other parts of the body.
Usually, brain tumors can be classified into 4 degrees according to their growth rate:
- Grade 1 and 2 brain tumor : A slow-growing brain tumor that rarely spreads to other regions of the brain. Usually, benign brain tumors, such as glioblastoma or meningioma;
- Grade 3 and 4 brain tumor : It is usually a malignant brain tumor that shows rapid growth.
The brain tumor rarely goes into metastasis, meaning it spreads to other parts of the body. Usually malignant cells develop and proliferate in the brain itself. Most brain tumors are benign and have well defined limits, that is, they have healing, and can be easily treated by chemotherapy, radiotherapy or surgically removed.
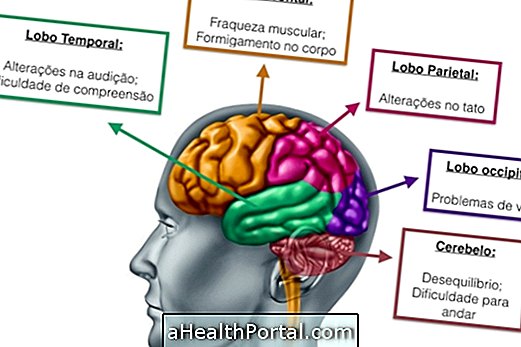
Main symptoms
The symptoms of brain tumor varies according to the region of the affected brain, the main ones being:
- Headache, which becomes more severe and frequent;
- Nausea and vomiting for no apparent reason;
- Changes in vision, such as blurred vision or double vision, for example;
- Frequent tingling in the arms or legs;
- Difficulty maintaining balance;
- Frequent seizures;
- Difficulty speaking or listening;
- Sudden changes in personality.
In addition, there may be difficulty walking and maintaining balance and changes in vision, such as blurred or double vision, which may be confused with ophthalmic problems, such as myopia or astigmatism. See other brain tumor symptoms.
The diagnosis by a neurologist according to the symptoms presented by the person and imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scan. From these examinations, the size and location of the tumor can be identified, and the best form of treatment, usually surgical, may be indicated. In addition, after surgical removal of the tumor, biopsy is performed to check whether the tumor has benign or malignant characteristics.
Types of brain tumor
The brain tumor can be classified into two types according to the origin of malignant cells. Primary tumors are those whose cells originate from the nervous system itself, the main types of primary brain tumor being:
- Meningioma: It is characterized by the presence of tumor in the meninges, which are membranes that surround and protect the central nervous system;
- Glioblastoma: A type of brain tumor that strikes glial cells, which are responsible for assisting in the functions of neurons - see how to identify and treat glioblastoma;
- Astrocytoma: This type of primary tumor reaches the cells that support the neurons and has variable gravity according to its size and characteristics, and can be benign or malignant;
- Medulloblastoma: The most common type of brain tumor in children, it affects the cerebellum and is usually benign;
- Pituitary adenoma: It is characterized by the involvement of the gland at the base of the brain, the adenohypophysis, causing effects on the whole organism.
Secondary tumors, on the other hand, are those whose cells come from tumors located in other parts of the body and that are metastasized, such as cancer of the lung, breast, kidneys and colon, for example.

How is the treatment done?
The treatment for tumor in the brain depends on the size, location, type of tumor, besides the age and the general state of the person and is done by a neurology through surgery, chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are mainly used to treat large or malignant tumors, and should be used over several months until the brain tumor has diminished or disappears. Usually, this type of treatment causes strong side effects such as tiredness, nausea, vomiting, hair loss or migraines, for example.
Already the surgery is used when the brain tumor is small and is separated from the brain tissue, and can be easily removed without affecting the functioning of the brain. This type of treatment has a greater risk of cerebral sequelae, such as paralysis or difficulty speaking, and therefore the patient may need to undergo physical therapy. Understand more about treatment for the tumor in the brain.