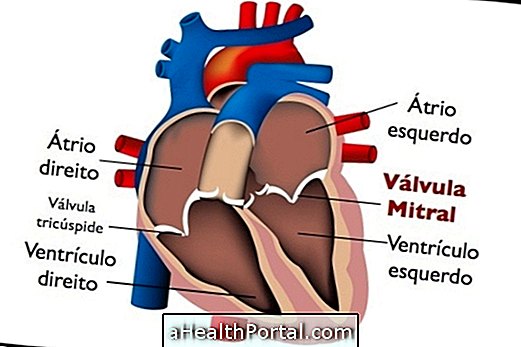
The functioning of the heart can be evaluated by a great diversity of examinations, each with its functions, which are chosen by the cardiologist or general practitioner according to each case.
Some tests, such as electrocardiogram, chest x-ray or ABPM, can be done routinely for check-up, while other tests, such as scintigraphy or holter, are done in cases of investigation of specific diseases such as angina or arrhythmias.

Thus, the main tests to evaluate the heart, are:
1. Chest x-ray
An X-ray or chest X-ray is an examination that looks at the contour of the heart and aorta, which is the vessel that leaves the heart to carry blood to the rest of the body. This exam is usually done with the patient standing, and with the lungs filled with air, to obtain the image, which is a kind of photograph.
- What is it for : evaluating enlarged heart or blood vessels, or detecting calcium deposition in the valves, which happens with age, as well as evaluating lung conditions, noting the presence of fluids and secretions.
- When it is contraindicated : it should not be done in pregnant women, especially in the first trimester and due to the emission of radiation, but if it is very necessary, it should be done with the protection of the belly with a lead apron. Understand the risks of x-rays in pregnancy.
Radiography is a superficial examination for a first examination, and other tests may be necessary to better evaluate the heart with more definition if the cardiologist feels it is necessary.
2. Electrocardiogram
It is an examination that evaluates the heart rate, and is done with the patient lying down, placing cables and small metallic contacts on his chest skin, to detect each beat, and is an initial examination to evaluate the functioning of the heart.
- What is it for : detect arrhythmias or irregular beats of the heart, and also changes in the functioning of heart valves and muscles, and for this reason, it is widely used as an initial evaluation for the infarction.
- When it is contraindicated : anyone can take this test, but it should not be done when the metal can not stick to the skin, because of an allergy, or when the person can not stand still, as this may alter the result.
The electrocardiogram is not painful, besides being very fast, and is often done by the cardiologist himself in the office. Understand more details of how the electrocardiogram is done.
3. MAP
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring, known as ABPM, is performed for 24 hours with a blood pressure monitor in the arm and a small waist-mounted tape recorder, which measures at intervals determined by the cardiologist and does not require hospitalization .
- What is it for : investigating pressure variation throughout the day, when there is doubt whether the patient has high blood pressure, or if there is suspicion of white-coat hypertension, which is when the pressure goes up during the medical visit but not at other times . It also serves to assess whether pressure-relieving medicines are working well throughout the day and night.
- When it is contraindicated : ABPM can not be done when it is not possible to adjust the cuff on the patient's arm, which can happen in very thin or obese people, and also in situations in which it is not possible to measure the pressure of shape reliable, which can happen in people who have tremors or arrhythmias, for example.
All blood pressure results that have been recorded will then be reviewed by the physician, and therefore it is recommended to maintain normal day-to-day activities as well as jot down in a diary what you were doing at each time the pressure was measures such as eating, walking or climbing stairs can change the pressure. Know the price and the care that one must have to do the MAPA

4. Holter
Holter is an examination to assess the heart's rhythm throughout the day and night, through a portable recorder that has the same electrodes on the electrocardiogram and a tape recorder that is attached to the body, recording each heartbeat of the period.
- What it is for : This test detects cardiac arrhythmias that may occur at various times of the day, investigates symptoms of dizziness, palpitation or fainting that may be caused by heart mismatch, and also evaluates the effect of pacemakers or remedies to treat arrhythmias.
- When it is contraindicated : this test can be done by anyone, but it should be avoided in people with skin irritations that alter the fixation of the electrocardiogram.
Although the period for the examination is 24 hours, there are more complicated cases that require 48h or up to 1 week for correct investigation of the heart rhythm. During holter it is also appropriate to note the activities in a diary, such as eating or making some effort, as they may interfere with the heart rate. 5.
5. Stress test
Also known as a treadmill test or exercise test, this test looks at changes in blood pressure or heart rate during exertion, which may be a treadmill or exercise bike.
- What it is for : Evaluating the functioning of the heart during exertion, detecting presence of chest pain, shortness of breath or arrhythmias, which may indicate a risk for infarction or heart failure.
- When it is contraindicated : This test should not be performed by patients who have physical limitations, such as walking or cycling, or who have an acute illness, such as an infection, which may alter the person's physical capacity.
The stress test evaluation imitates situations required by the body, such as climbing stairs or a slope, for example, which are situations that can cause discomfort or shortness of breath in those at risk for heart attack. Learn more about stress testing.
Echocardiogram
Also called a Doppler echocardiogram, it is a kind of heart ultrasound that detects images during your activity, assessing their size, the thickness of their walls, the amount of blood pumped, and the functioning of the heart valves.
- What it does : evaluate the functionality of the heart, detecting heart failure, heart murmurs, changes in the shape of the heart and vessels, and can detect the presence of tumors inside the heart.
- When it is contraindicated : the examination can be difficult in people with breast implants or obesity.
This examination is painless, and does not use x-ray to obtain its image, so it is very accomplished and provides many important information about the patient's heart. It is often done to investigate people who have shortness of breath to the exertion and swelling in the legs, which may indicate an insufficiency of the heart. See the step-by-step procedure for performing the echocardiogram.

7. Myocardial scintigraphy
Scintigraphy is an examination done by injecting a contrast into the patient's vein, which captures images of the vessels, to make a complete evaluation of the circulation in the heart.
- What is it for : to evaluate changes in blood irrigation in the heart, as can happen in angina or infarction, for example. He is also able to observe the functioning of heartbeats and muscles.
- When it is contraindicated : in people with allergy to the active principle of contrast, people with severe arrhythmias or with kidney problems, since the elimination of contrast is done by the kidneys.
The cardiologist can also decide whether this test will be performed with or without the stimulation of medications that accelerate the heart rate to mimic a patient's stress situation. See how the preparation is done for scintigraphy.
Laboratory tests to evaluate the heart
There are some blood tests that may be ordered to evaluate the heart, such as Troponin, CK and CK-MB, for example, that may be altered during a heart attack.
Other tests, such as glycemia, cholesterol and triglycerides, solved at cardiovascular check-up, for example, although not specific to the heart, indicate that if there is no control, with medication, physical activity and balanced diet, there is a great risk of developing a cardiovascular disease in the future. Understand better when to have a cardiovascular checkup.