Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is a type of lymphatic cancer characterized by the enlargement of some lymph nodes and the most common type is what strikes type B defense cells. Its symptoms may include night sweats, fever and itchy skin and your treatment is made with chemotherapy, radiotherapy and immunotherapy.
The choice of treatment depends on the size of the tumor, its location and whether there are metastases or not. Although severe, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma can be cured by performing the treatment.
Symptoms of Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
The symptoms of this type of cancer can arise at any stage of life, are more common in men and are usually:
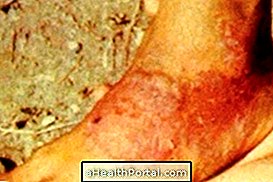
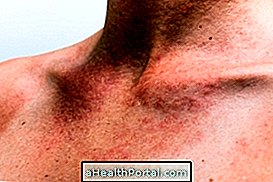
- Enlargement of the lymph nodes;
- There may be a fever;
- There may be weight loss;
- There may be night sweats of great intensity;
- There may be itching of the skin.
No specific cause has yet been identified for the development of this lymphoma but there is a suspicion that the immune system involved and the onset of various infections are related to the disease. Learn more about Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma Symptoms.
Types of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
There are more than 40 types of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and they are further classified according to the cells that affect: B or T, and also consider tumor size, shape and presentation under the microscope, but usually non-Hodgkin's lymphomas are subdivided into: indolent or aggressive because knowing this is extremely important so that the treatment is really well targeted.
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma can be classified as:
- Type I: Only one lymph node is affected;
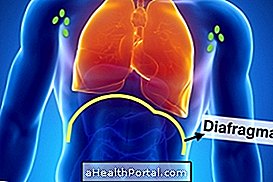
- Type II: More than one lymph node is affected, but all are located on the same side of the diaphragm;
- type III: Abdominal lymph nodes affected;
- type IV: Various lymph nodes affected throughout the body.
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma should still be classified as indolent when its development is slow, with no symptoms, or aggressive when its development is rapid and has symptoms.
The physician can identify the type of lymphoma that the person has and his staging by requesting tests such as complete blood count, renal and hepatic function, calcium, uric acid, computed tomography of the chest, abdomen and pelvis, and bone marrow biopsy.
Causes of Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Some of the possible causes of the development of this disease include weakness of the immune system, exposure to pollutants, high doses of radiation, immunosuppressive drugs and viral or bacterial infections. Epstein-Barr virus carriers as well as those with H. pylori bacteria in the stomach are at increased risk of developing some type of lymphoma.
The environment that the individual lives and their life habits also interfere in the way the body reacts to the harmful effects caused by exposure to chemical agents increasing the risk of developing this cancer.
Treatment of Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Treatment can be done through chemotherapy and associated radiotherapy, but the use of monoclonal antibodies has also been shown to be effective. However, the choice of treatment depends on lymphoma staging and should be indicated by the oncologist. Learn the remedies, diet and tips to combat this tumor here.
The prognosis of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma varies depending on the extent of disease and the affected organs. When it is discovered early there is a greater chance of cure, but when the lymphoma is at a more advanced stage and there is metastasis the cure may be more difficult, but usually aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, though more severe, are more likely to cure. Find out what are the chances of healing this tumor here.