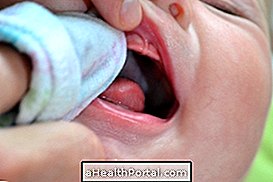
Buruli ulcer is a skin disease caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium ulcerans, which leads to the death of skin cells and surrounding tissues, and can also affect bone, resulting in the appearance of wounds that grow slowly without causing pain.
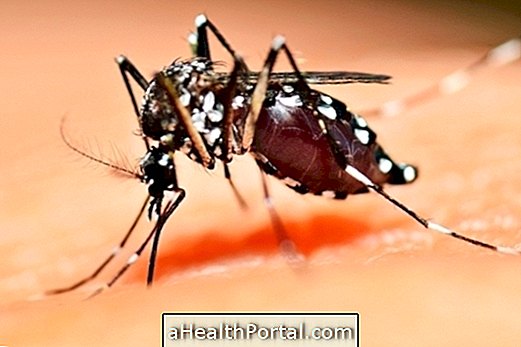
Although the form of transmission of this disease is not known, the main possibilities are that it is transmitted by drinking contaminated water or by the bite of some mosquitoes or insects.
It is important that buruli ulcer be treated according to the doctor's guidance, with antibiotics, as it is thus possible to prevent it from continuing to develop and cause complications, such as deformations and generalized infection.

Buruli ulcer symptoms
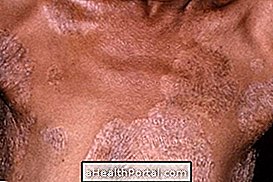
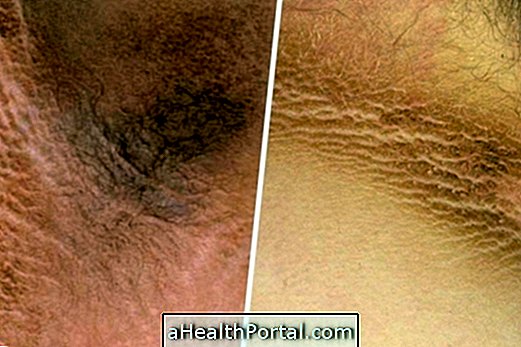
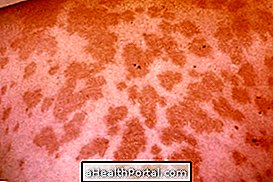
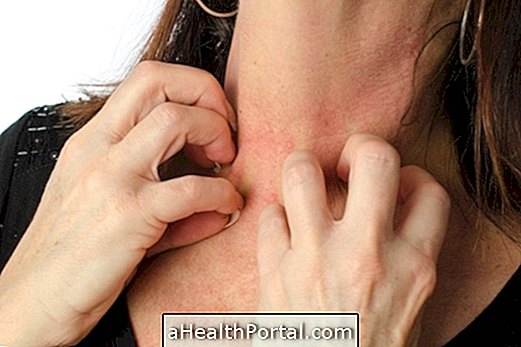
The ulcer begins with a painless lump that slowly progresses to the ulcer and usually appears on the arms and legs. Other symptoms that may be present are:
- Swelling of the skin;
- Sore that grows slowly without causing pain;
- Darker colored skin, especially around the wound;
- Swelling of the arm or leg, if the wound appears on the limbs.
It is important that the general practitioner, dermatologist or infectious disease specialist is consulted as soon as the first symptoms of buruli ulcer appear, as it is possible that the treatment will be started soon afterwards to avoid the development of complications, such as deformities, secondary bacterial and bone infections. , for example.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis of buruli ulcer is made by a dermatologist, general practitioner or infectious disease based on the observation of symptoms and assessment of the person's history, especially when living in regions where there is a high number of cases.
In addition, a biopsy of the affected tissue is usually indicated to identify the presence of the bacteriaMycobacterium ulcerans and performing a wound culture to check for secondary infections, in addition to being useful for confirming the diagnosis.
How the treatment is done
In most cases, the infection is identified when it is poorly developed and affects an area of less than 5 cm. In these cases, treatment is done only with the use of antibiotics, such as Rifampicin associated with Streptomycin, Clarithromycin or Moxifloxacin, for 8 weeks.
In cases where the bacterium affects a more extensive region, the doctor may need to have surgery to remove all the affected tissue and even correct deformations, in addition to making treatment with antibiotics. In these cases, assistance from a nurse may also be necessary to treat the wound in an appropriate manner, thus accelerating healing.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther
Bibliography
- PAN AMERICAN HEALTH ORGANIZATION. Recognition of tropical diseases neglected by skin changes. Available in: . Accessed on 29 Mar 2021