Maffucci Syndrome is a rare disease that affects the skin and bones, causing cartilage tumors, deformities in the bones and appearance of dark tumors in the skin caused by abnormal growth of blood vessels.
The causes of Maffucci Syndrome are genetic and affect men and women alike. Usually, the symptoms of the disease develop in childhood around 4-5 years of age.
Maffucci Syndrome has no cure, but patients may receive treatment to decrease the symptoms of the disease and improve their quality of life.
Symptoms of Maffucci Syndrome
The main symptoms of Maffucci Syndrome are:
- Benign tumors in the cartilage of the hands, feet and long bones of the arm and legs;
- Bones become brittle, easily fractured;
- Bone shortening;
- Hemangiomas, which consist of small dark or blue bluish tumors on the skin;
- Short;
- Lack of muscle.
Individuals with Maffucci Syndrome may develop bone cancer, especially in the skull, but also cancer of the ovary or liver.
The diagnosis of Maffucci Syndrome is made through physical examination and analysis of the symptoms presented by the patients.
Treatment of Maffucci Syndrome
The treatment of Maffucci Syndrome consists of minimizing the symptoms of the disease through surgery to correct bone deformities or supplements to aid in the growth of the child.
Individuals affected by the disease should regularly consult the orthopedic doctor to assess changes in bone, bone cancer development and treat fractures that occur due to disease. The dermatologist should also be consulted to evaluate the appearance and development of hemangiomas in the skin.
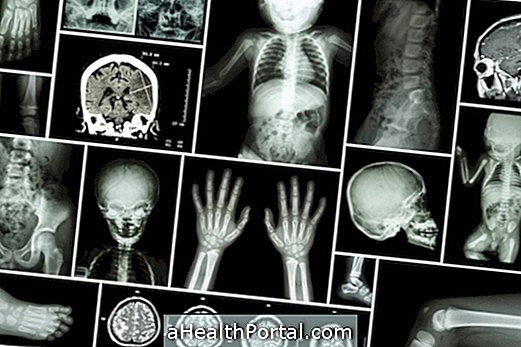
It is important for patients to have regular physical exams, X-rays, or CT scans.
Pictures of Maffucci Syndrome
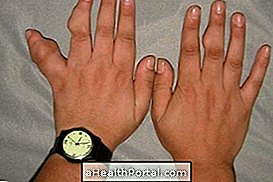

Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Photo 1: Presence of small tumors in the joints of the fingers characteristic of the Maffucci Syndrome;
Photo 2: Hemangioma in the skin of a patient with Maffucci Syndrome.
Useful link:
- Hemangioma
- Proteus Syndrome