Bartholin's glands are glands that lie at the entrance of the vagina on either side of the labia minora and are responsible for releasing a lubricating fluid.
Bartolotomy consists of removal of the Bartholin's glands, when they are often clogged, causing cysts and abscesses. Usually only this medical procedure is used as a last resort, when no other less invasive treatment works. Learn about the causes, symptoms, and treatment of Bartholin's cyst.
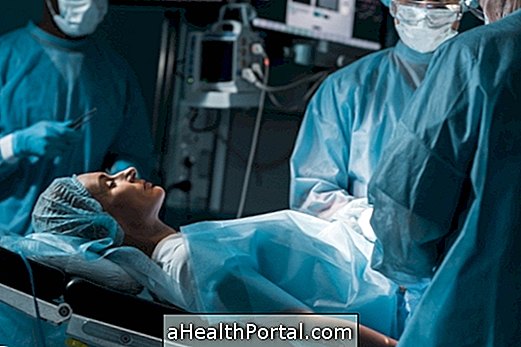
What is surgery?
Surgery consists of removal of the Bartholin gland. This should be the last resort treatment option if other treatments such as antibiotics and drainage of the cysts and abscesses are ineffective and if the person has multiple episodes of cysts and abscesses.
Usually, the surgery is performed under general anesthesia and takes about an hour to be performed. In the postoperative period, the person should stay in the hospital for 2 to 3 days.
Caring for Recovery
In order for healing to take place correctly and to reduce the risk of infection after surgery, the following should be avoided:
- Have sexual reactions for 4 weeks;
- Use internal absorbent for 4 weeks;
- Conduct or perform tasks that require some concentration within 48 hours following general anesthesia;
- Use hygiene products on the spot that have scented additives.
Learn 5 rules for doing intimate washing and avoiding illness.
What are the risks of surgery?
The risks of this type of surgery include bleeding, bruising and infection at the site where the surgery is performed. In case of infection, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics for treatment.