Mastectomy is a surgical procedure for the removal of one or both breasts, which is most often indicated for people diagnosed with cancer, and may be partial when only part of the tissue is removed, when the breast is removed completely or even radical when, in addition to the breast, nearby muscles and tissues that may have been affected by the tumor are removed.
In addition, mastectomy can also be preventive, to decrease the risk of women developing breast cancer, or may have an aesthetic intent, in the case of surgery with masculinizing intent, for example.
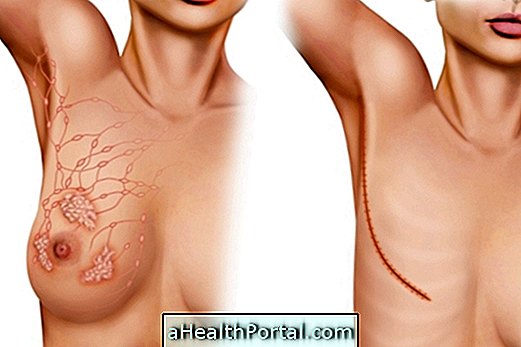
Types of mastectomy
For each goal that one wishes to achieve with the withdrawal of the breast, a type of surgery can be done, which is chosen by the mastologist or plastic surgeon, according to each case. The main types are:
1. Partial mastectomy
Also called a quadrantectomy or sectorectomy, it is a surgery to remove a nodule or benign tumor, with part of the tissue around, without the need for total withdrawal of the breast.
In this surgery, some nearby nodes may be removed from the breast to avoid risk of the nodule returning.
2. Total or simple mastectomy
In total mastectomy the mammary glands are removed completely, in addition to the skin, areola and nipple. It is best indicated in case of small tumor, discovered early and well located, without the risk of having spread to surrounding regions.
In this case it is also possible to remove or not ganglia in the armpit region, to decrease the risk of the tumor coming back or spreading.
3. Radical mastectomy
In radical mastectomy, in addition to the removal of the entire breast, the muscles located underneath it and the ganglia of the axilla region are also removed, being indicated for cases of cancer with risk of dissemination.
There are variants of this surgery, known as modified radical mastectomy of Patey, in which the pectoralis major muscle is maintained, or modified radical mastectomy of Madden, when both the major and minor pectoralis muscles are preserved.
4. Preventive Mastectomy
Preventive mastectomy is done to prevent the development of cancer, and is indicated only for women at very high risk for this disease, such as those who have a significant family history or who have genetic alterations that can cause cancer, known as BRCA1 and BRCA2. Know when to take the genetic test for breast cancer.
This surgery is done in a similar way to total or radical mastectomies, being removed all the breast, nearby nodes and in some cases, the surrounding muscles. Generally, bilateral surgery is done because in these cases, the risk of developing cancer is similar in both breasts.
5. Other types of mastectomy
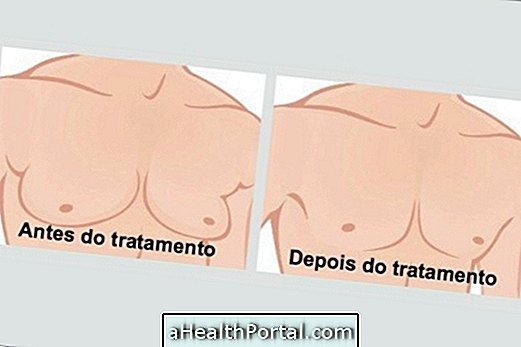
Male or masculinizing mastectomy is a type of plastic surgery designed to give a woman a masculine appearance. Thus, in this surgery, the removal of the breasts is done, which may be by different techniques, decided by the plastic surgeon, depending on the size and type of breasts of each woman.
Mastectomy can also be performed in cases of breast cancer in man, which happens more rarely, and surgeries are done the same way as in women, although the man has much fewer glands.
There are also cosmetic breast surgeries are known as mammoplasty, which may aim to reduce, increase or improve the appearance of breasts. Learn about breast plastic surgery options.
Mastectomy Price
The price of surgery can vary from R $ 10, 000.00 to R $ 20, 000.00, depending on the type of surgery and the site performed.
How is the postoperative
The breast lift surgery is a surgery lasting about 60 to 90 minutes, with spinal or general anesthesia.
Recovery after the procedure is rapid and may require 1 to 2 days of hospitalization, depending on the type of surgery and whether it was bilateral or unilateral.
A drain may be left, so that the secretion produced in the first few days after the procedure is withdrawn, which should be securely attached to the clothing so that it is not pulled accidentally. This drain should be emptied about 2 times a day, with an annotation of the amount drained to inform the doctor at the return visit.
In addition, some recommendations that should be followed in the postoperative period are:
- Taking painkillers or anti-inflammatory drugs as prescribed by your doctor in case of pain;
- Go to the return visit, usually scheduled after 7 to 10 days of the procedure;
- Do not take weight, drive or exercise during this period or until medical release;
- Contact your doctor in case of fever, severe pain, redness or swelling at the surgery site or on the arm on the operated side;
In operations with withdrawal of the lymph nodes, the circulation of the corresponding arm can be compromised, and it becomes more sensitive, being important to protect it well from injuries, burns and avoid excessive efforts.
After the procedure, it is still important that treatment be continued with physical therapy, which will help to improve arm movements, circulation, and decrease contractures caused by scarring. See more details on recovery after breast removal.
How and when to perform breast reconstruction
After performing any type of mastectomy, breast reconstruction surgery may be necessary to regain the natural shape of the breasts. It can be done immediately after the procedure or in stages, with gradual correction of the region, but in many cases of cancer, it may be necessary to wait some time until the total scarring or after the tests to confirm the complete removal of the malignant cells .
See more about how breast reconstruction is done.


Who should do mastectomy
Mastectomy can be performed when:
- The woman is at high risk of developing breast cancer (preventive mastectomy);
- It is necessary to complement the radiotherapeutic and chemotherapeutic treatment for breast cancer;
- One can prevent breast cancer in the other breast when the woman has had cancer in one breast;
- The woman has carcinoma in situ, or located, discovered early to prevent disease progression;
- There is the desire to remove the breasts, as in the masculinizing mastectomy.
Thus, it is important for the woman to consult with the gynecologist annually for preventive evaluations, or whenever symptoms arise that may indicate the presence of a breast tumor, such as presence of a lump, redness or presence of secretion in the breasts. Learn to recognize the main symptoms of breast cancer.