Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects white blood cells, also known as leukocytes, which are the body's defense cells. This disease begins in the bone marrow, which the inner part of the bone, popularly known as 'bone marrow' and spreads through the body through the blood, preventing or disrupting the production of red blood cells, platelets and white blood cells, and because of this anemia, infections and hemorrhages.
Leukemia is a serious illness that needs treatment, which can be done with chemotherapy, radiation therapy or bone marrow transplantation, for example. The choice of treatment varies according to the type of leukemia that the person has and its severity, which also determines whether the person can be completely cured or not.
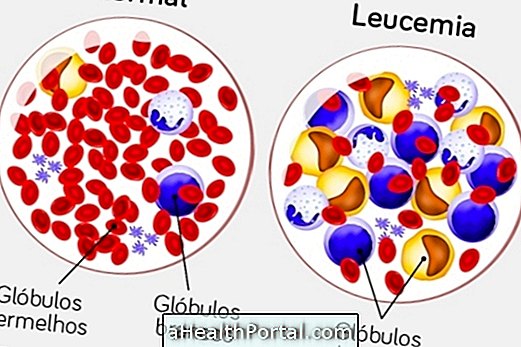
Types of Leukemia
There are 2 main types of leukemia, lymphoid and myeloid, which can be classified as being acute or chronic, but there are still 4 other subtypes, as follows:
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia: It develops rapidly and may also affect adults or children. Treatment can be done through chemotherapy and / or bone marrow transplantation and has an 80% chance of cure.
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: It develops slowly and is more common in adults. Treatment can be done with the use of specific medications for a lifetime.
- Acute Lymphoid Leukemia: Fast forward and can occur in children or adults. Treatment can be done with radiotherapy and chemotherapy, but bone marrow transplantation is also an option when previous treatments fail to cure the disease.
- Chronic Lymphoid Leukemia: It develops slowly and affects the elderly more often. Treatment is not always necessary.
- Granular lymphocytic leukemia T or NK: This type of leukemia is slow growing, but a small number may be more aggressive and difficult to treat.
- Aggressive NK Cell Leukemia: It can be caused by the Sptein-Barr virus, it affects teenagers and young adults, being aggressive. The treatment is done with chemotherapy.
- Adult T-cell leukemia: It is caused by the virus (HTLV-1), a retrovirus similar to HIV, being very serious. Treatment is poorly effective but is done with chemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation.
- Hairy Cell Leukemia: It is a type of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, which affects cells that appear to have hairs, affects most men, not being found in children.
The type of leukemia that the person has is determined through specific tests, being essential to know which treatment is most indicated.
Symptoms of leukemia

The first symptoms of leukemia are high fever followed by chills, night sweats and weight loss with no apparent cause, then other symptoms may appear, such as:
- Inflamed tongues in the neck, armpits and just behind the elbow bone, technically called elbow fossa, which is one of the characteristics of the disease;
- Enlargement of the spleen causing pain in the upper left region of the abdomen;
- Anemia that causes symptoms such as tiredness, pallor and drowsiness;
- Low concentration of platelets in the blood;
- Infections, such as oral candidiasis, and in the stomach (thrush) or atypical pneumonia;
- Pain in bones and joints;
- Night sweats;
- Purple spots on the skin;
- Pain in bones and joints;
- Easy bleeding from the nose, gums or heavy menstruation with no apparent cause.
- Headache, nausea, vomiting, double vision and disorientation occur when the central nervous system is affected.
These symptoms are more common in acute leukemia, because as chronic leukemia progresses slowly, it can be asymptomatic and discovered on a routine examination as a complete blood count, for example.
Diagnosis of leukemia
The diagnosis is made by the hematologist or oncologist after observing some signs and symptoms and with the results of exams such as hemogram, myelogram, computed tomography, magnetic resonance and more specifically, bone marrow biopsy. In some cases it may be necessary to have the CSF examined, called a lumbar puncture, to evaluate the fluid that lines the central nervous system.
Treatments for Leukemia

Leukemia can be treated with the following options: chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy, bone marrow transplantation, or the combination of different treatments, depending on the type of leukemia the person has, and the stage of the disease.
In the case of acute leukemia treatment should be started as soon as possible to combat the symptoms and prevent the disease from worsening. Many cases can be completely cured, with the treatments indicated by the doctor. In the case of chronic leukemia, the disease may not show symptoms, but can hardly be cured, although the person may have a 'maintenance' treatment to avoid the manifestation of symptoms throughout life and to keep this type of cancer controlled.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy consists of the application of specific drugs against cancer, which can be injected directly into the vein during hospitalization. This treatment is usually done in cycles, because they are performed once a week with only 1 drug, or a combination of 2 or 3. In some cases the sessions can be performed with interval of weeks or months.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a treatment similar to chemotherapy, because it consists in the application of drugs directly into the vein, but these drugs act differently, and are monoclonal antibodies, which are substances that bind to cells
allowing the body's defense system to eliminate tumor cells in the blood and bone marrow.
Radiotherapy
It consists of the application of radiation directed to the spleen, brain or other parts of the body, in some cases it can be directed to the whole body, as it happens before a transplant of bone marrow, for example.
Bone marrow transplant
Bone marrow transplantation consists of removing a portion of the bone marrow from the hip of a healthy person and compatible with the sick person, and these are frozen until they can be used at the ideal time. The ideal time to put the donated bone marrow is decided by the doctor, and can happen after finishing the chemo and radiotherapeutic treatments. The goal is to take the place of malignant cells and re-produce healthy blood cells.

Does leukemia have a cure?
In some cases leukemia is curable, especially when it is diagnosed early and treatment is instituted quickly, however there are cases where the individual's body is already so weak that cure of the disease is difficult to achieve. Bone marrow transplantation may represent the cure of leukemia for some, but it does have complications and so it is not always an option indicated by doctors for all those affected.
Some patients with acute leukemia now achieve complete remission of the disease and last for many years, and many children with acute lymphocytic leukemia can be cured. Ideally, talk to the doctor who is following the case to see what the next steps in treatment will be and what to expect.
What Causes Leukemia
The causes of leukemia are not fully understood but what is known is that some genetic preconditions favor the development of this disease. Leukemia is not hereditary and is only a father to child, nor is it contagious and so it does not pass to other people. Some factors that can cause leukemia to occur include radiation effects, exposure to drugs, including cigarettes, immune factors, and certain types of virus.