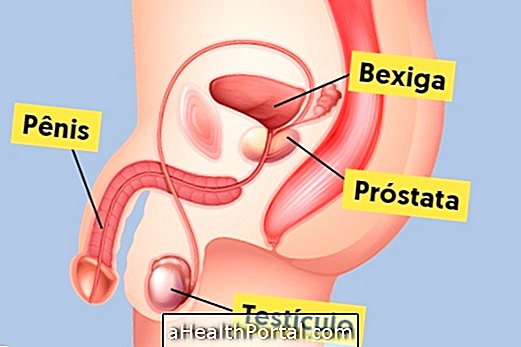
Amputation of the penis, also known scientifically as penectomy or falectomy, occurs when the male sexual organ is completely removed, known as total, or when only a portion is removed, known as partial.
Although this type of surgery is more frequent in cases of penile cancer, it may also be necessary after accidents, trauma and serious injuries, such as suffering a severe stroke in the intimate region or being a victim of mutilation, for example.
Already in the case of men who intend to make sex alteration, the removal of the penis is not called amputation, since plastic surgery is done to recreate the female sexual organ, and is then called neofaloplasty.
1. Is it possible to have sex?
The way penile amputation affects intimate contact varies according to the amount of penis removed. Thus, men who have suffered a total amputation may not have enough sex organ to have a normal vaginal relationship, however, there are different sex toys that can be used instead.
In the case of a partial amputation, it is usually possible to have intercourse again in about 2 months, as soon as the region is well healed. In many of these cases, the man has a prosthesis, which was inserted into the penis during surgery, or what remains of his penis is still sufficient to maintain the pleasure and satisfaction of the couple.
2. Is there a way to rebuild the penis?
In cancer cases, during surgery, the urologist usually tries to preserve as much of the penis as possible so that it is possible to reconstruct what is left through a neofaloplasty, using skin of the arm or thigh and prostheses, for example. Learn more about how penile prostheses work.
In cases of amputation, in the vast majority of cases, the penis can be reconnected to the body, provided it is done in less than 4 hours, to avoid death of the entire penile tissue and ensure higher success rates. In addition, the final look and success of the surgery may also depend on the type of cut, which is best when it is a clean and clean cut.
3. Does amputation cause a lot of pain?
In addition to the very intense pain that can occur in cases of amputation without anesthesia, as in cases of mutilation, and may even cause fainting, after recovery many men may feel a phantom pain where the penis was. This type of pain is very common in amputated people, because the mind takes a long time to adapt to the loss of a limb, eventually creating discomfort during the day as tingling in the amputated region or pain, for example.

4. Does the libido remain the same?
The sexual appetite in man is regulated through the production of the hormone testosterone, which happens mostly in the testicles. Thus, men who do amputation without removing the testicles may continue to feel the same libido as before.
Although it may seem a good point, in the case of men who have suffered a total amputation and who can not do reconstruction of the penis, this situation can cause great frustration, since they have greater difficulty to respond to their sexual will. Thus, in these cases, the urologist may recommend removing also the testicles.
5. Is it possible to have an orgasm?
In most cases, men who have undergone amputation of the penis may have an orgasm, however, it may be more difficult to attain, since the vast majority of nerve endings lie in the head of the penis, which is usually removed.
However, mind stimulation and touching the skin around the intimate region may also be able to produce an orgasm.
6. How do you use the bathroom?
After removing the penis, the surgeon tries to rebuild the urethra so that the urine continues to flow out the same way as before, without causing changes in the man's life. However, in cases where it is necessary to remove the entire penis, the urethral orifice can be replaced underneath the testicles and, in such cases, it is necessary to eliminate urine sitting in the toilet, for example.