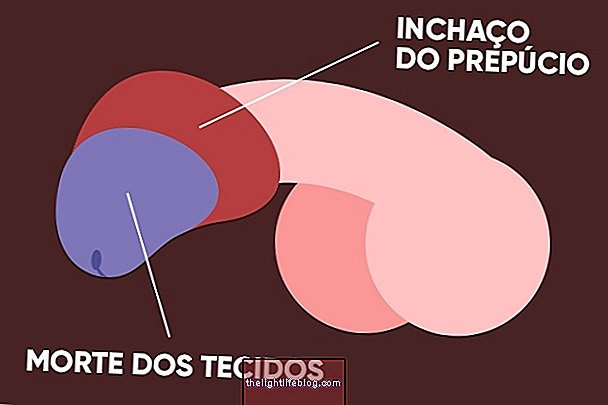
Testicular rupture occurs when there is a very strong blow to the inner region that causes the outer membrane of the testicle to rupture, causing severe pain and swelling of the scrotum.
Typically, this type of injury is more common in only one testicle and in athletes who practice high-impact sports, such as football or tennis, for example, but can also happen due to traffic accidents when the testicle is pressed too hard against the testicles. bones of the pelvic region, especially in motorcycle accidents.
Whenever a testicle is suspected, it is recommended that you go to the emergency room immediately for an ultrasound examination and to evaluate the structure of the testicles. If there is rupture it is necessary to have surgery to correct the injury.
Main symptoms
Testicular rupture usually causes very intense symptoms, such as:
- Very strong pain in the testicles;
- Swelling of the scrotum;
- Increased tenderness in the testis region;
- Hematoma and purple spot on the testicles;
- Presence of blood in the urine;
- Uncontrollable desire to vomit.
In some cases, due to the very strong pains in the region of the testicles also it is common that the man faints. Due to all these symptoms more intense than a simple blow, it is usually easy to identify that it is necessary to go to the hospital.
When the rupture is identified and treated in the first few hours there is a greater success rate to repair the injury without having to completely remove the affected testicle.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment of testicular rupture should be guided by a urologist, however, it is almost always necessary to undergo general anesthesia to stop bleeding, remove tissue from the dying testicle, and close the rupture in the membrane.
In more severe cases, the testicle may become very affected and therefore, before starting the surgery the doctor usually asks permission to remove the affected testicle if necessary.
How is recovery from surgery?
After surgery for testicular rupture you need to keep a small drain in the scrotum, which consists of a thin tube that helps to remove excess fluid and blood that may accumulate during the healing process. This drain is usually removed after 24 hours before the patient returns home.
After discharge, you need to take the antibiotics prescribed by the urologist, as well as anti-inflammatories, not only to relieve discomfort but also to speed recovery. It is also advised to keep as much rest as possible in bed and apply cold compresses whenever necessary to reduce swelling and improve pain.
The post-surgery review appointment usually takes place after 1 month and serves to assess the condition of healing and to receive guidance on the types of exercises that can be done.