Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease that leads to the formation of atheroma (fat) plaques within the blood vessels, causing serious consequences when present in coronary vessels. The most frequent symptoms resulting from the presence of atherosclerotic disease in the heart are chest pain or discomfort, and may radiate to the neck, arms, belly and upper back. In addition to pain, the patient may also feel tired after exertion, shortness of breath and weakness.
Depending on the severity and size of the plaques, the disease can remain symptom free, silently for several years.
Causes of atherosclerosis
The causes of atherosclerosis are the accumulation of plaques of fats and other substances in the arteries of the heart. This accumulation leads to narrowing of the arteries, resulting in a decrease or interruption of blood flow to the heart, resulting in what we call angina or infarction, depending on its severity.
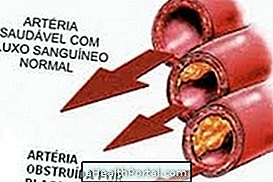
Learn more at: Causes of Atherosclerosis.
Treatment for atherosclerosis
Treatment for atherosclerosis will depend on the symptoms and severity of the disease.
Some medications that are part of the treatment of atherosclerotic disease are:
- Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors: lower blood pressure and protect the heart and kidneys;
- Aspirin: prevent plaque formation in the arteries;
- Beta blockers: reduce heart rate and lower blood pressure, decreasing cardiac work;
- Calcium channel blockers: relax arteries, lower blood pressure and reduce strain in the heart;
- Diuretics: lower the pressure and treat heart failure;
- Nitrates: relieve chest pain and improve blood flow to the heart;
- Statins: reduce cholesterol and plaque formation;
In addition to the remedies, you can adopt a healthier lifestyle through the measures described below:
- Avoid drinking alcoholic beverages;
- Do not smoke;
- Exercise at least 30 minutes a day;
- Reduce weight;
- Maintain a balanced diet;
- Avoid salt and fats.
In certain cases where atheroma or fat plaques have obstructed more than 80% of the lumen of the vessel, invasive treatment with angioplasty with stent or balloon, or even revascularization surgery with the placement of the saphenous or mammary bridges is necessary.