Vitamin B6, also called pyridoxine, plays roles in the body such as protecting neurons and producing neurotransmitters, substances important for the proper functioning of the nervous system. See all functions here.
This vitamin can be found in foods like meats, salmon, milk, eggs, lentils and spinach, and its deficiency causes the following symptoms in the body:
- Anemia;
- Tiredness and drowsiness;
- Problems in the nervous system, such as mental confusion and depression;
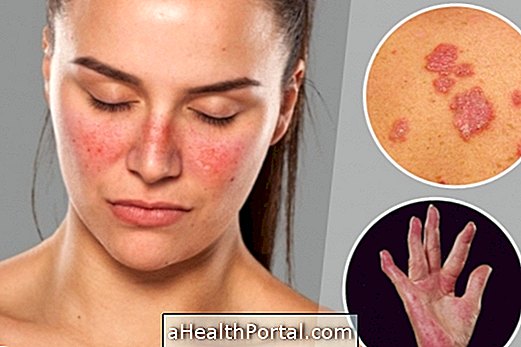
- Dermatitis and cracks in the corners of the mouth;
- Swelling in the tongue;
- Weakening of the immune system.

In children, vitamin B6 deficiency also causes irritability, hearing problems, and seizures. In addition, it is important to remember that normally the deficiency in this vitamin is also accompanied by lack of vitamins B12 and folic acid.
Risk factors
In some cases the risk of vitamin B6 deficiency in the body is greater, such as in people with kidney problems, celiac disease, Crohn's disease, intestinal ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis and in cases of excessive alcohol consumption.
Excess Vitamin B6
Excessive intake of vitamin B6 is rare and usually occurs due to the use of dietary supplements, and symptoms such as loss of control of body movements, nausea, heartburn, sensitivity to light and skin wounds can arise. However, these symptoms improve with the suspension of the use of vitamin supplementation. See more about the supplement here.
See the rich foods and all the functions of vitamin B6.