The most common symptoms that may indicate that the baby has tongue prey include:
- Difficulty in lifting the tongue up to the teeth from above;
- Difficulty in moving the tongue sideways;
- Difficulty in putting the tongue out, beyond the teeth underneath;
- Language in the form of a knot or heart when the child puts it out;
- The baby bites the mother's nipple instead of sucking it;
- The baby feeds badly and is hungry shortly after breastfeeding;
- The baby can not gain weight or grows more slowly than expected.
The tethered tongue, scientifically called the short tongue brake, is a genetic change, in which the piece of skin that connects the tongue to the mouth, called a bridle, is shorter and tight, making it difficult to move the tongue.
However, the imprisoned tongue is cured by surgery to curb the tongue, which is not always necessary because, in some cases, the tongue trapped disappears spontaneously or does not cause problems.
Photos of prey tongue
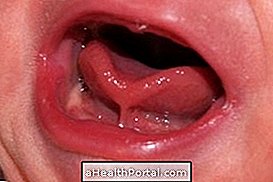

Problems Caused by Imprisoned Language
The tongue trapped in the baby can cause problems in breastfeeding, as the baby has a harder time sucking the breast properly, biting the nipple rather than sucking it, which is very painful for the mother. By interfering with breastfeeding, the tongue trapped also causes the baby to feed poorly, getting hungry very quickly after suckling and not gaining the expected weight.
In older children, the tongue trapped can cause difficulties in speech, interfere with oral hygiene, create space between the lower front teeth or even disrupt the kiss or play a wind instrument such as flute or clarinet.
How to treat tongue trap
The treatment of the arrested tongue is only necessary when the feeding of the baby is affected or when the child has problems in the speech, and is a surgery to cut off the language brake, so as to allow the movement of the tongue.
The surgery for tongue prey is quick and the discomfort is minimal, since there are few nerve endings or blood vessels in the tongue bracket, and after surgery, it is possible to feed the baby normally.
Speech-language pathology is also recommended when the child has speech difficulties, and after surgery, through exercises that improve tongue movement.