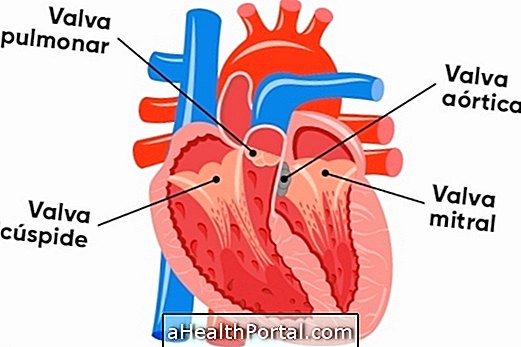
Stent angioplasty is a medical procedure performed with the goal of restoring blood flow by introducing a metal mesh into the clogged vessel. There are two types of stents:
- Pharmacological stent, in which there is progressively release of drugs into the bloodstream, decreasing the accumulation of new fat plaques, for example, in addition to being less aggressive and less risk of clot formation;
- Non-pharmacological stent, which aims to keep the vessel open, regulating blood flow.
The stent is placed by the doctor where the blood passes with difficulties, either due to a fat plate or due to the decrease in vessel diameter as a result of aging. This procedure is especially recommended in people with heart risks due to changes in blood flow.
Stent angioplasty should be performed with a cardiologist or vascular surgeon and costs approximately R $ 15, 000.00, however some health plans cover this expense, as well as being available through the Unified Health System (SUS).

How is it done?
Stent angioplasty is done under local anesthesia and consists of insertion of a catheter into an artery in the thigh or arm and that is positioned at the place where there is obstruction. The doctor then inflates the balloon and releases the stent, which is a metal plate, leaving the vessel open and restoring local blood flow.
The procedure lasts about 1 hour and is minimally invasive due to the help of a micro-camera that is normally coupled to the catheter so that the physician can identify the correct implantation site.
Check out the procedure:

Possible risks
Angioplasty is a very invasive and very safe procedure, with success rates between 90 and 95%. However, just like any other surgical procedure, it has its risks. One of the risks of stent angioplasty is that during the procedure the release of a clot occurs, resulting in a clot.
In addition, there may be bleeding, bruising, postoperative infections and, in more rare cases, bleeding, requiring blood transfusion. In some cases, even with stent implantation, the vessel may become clogged again, requiring the placement of another stent.
How is recovery
Recovery after stent angioplasty is relatively rapid. When surgery is not performed urgently, the person is usually discharged the next day with a recommendation to avoid strenuous exercise or lift weights above 10 kg within the first 2 weeks of angioplasty. In 2 to 3 days work and sexual activity can be resumed.
It is important to clarify that stent angioplasty does not prevent the accumulation of fat plaques inside the arteries and therefore it is indicated the regular practice of physical activity and a balanced diet to avoid the "clogging" of other arteries. In addition, the physician may recommend the use of some medication to lower cholesterol if the drug-eluting stent is not used.