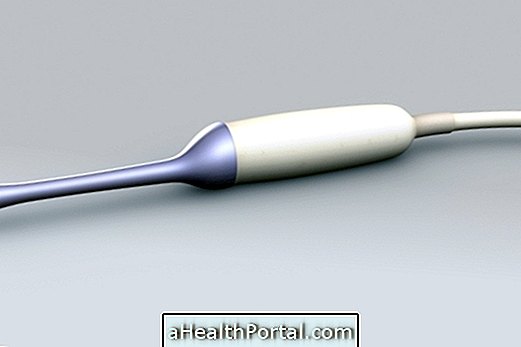
Transvaginal ultrasound, also known as transvaginal or transvaginal ultrasound, is a diagnostic test that uses a small device that is inserted into the vagina and produces sound waves that are then transformed by the computer into images of the internal organs, such as the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, cervix, and vagina.
Through the images produced by this examination it is possible to diagnose different problems of the pelvic region, such as cysts, infections, ectopic pregnancy, cancer or, even, confirm a possible pregnancy.
Since the ultrasound examination has several advantages, since it is not painful, it does not emit radiation and produces clear and detailed images, it is almost always one of the first examinations recommended by the gynecologist when it is necessary to evaluate the cause of some alteration in the reproductive system of the woman .
When to do it
In most cases, transvaginal ultrasonography is used to identify causes for symptoms such as pelvic pain, infertility or abnormal bleeding, with no apparent cause. However, it can also be advised when cysts or ectopic pregnancy are suspected, as well as for placing the IUD.
Already during pregnancy, this examination can be requested to:
- Identify first signs of possible miscarriage;
- Monitor baby's heart rate;
- Examine the placenta;
- Identify causes of vaginal bleeding.
In some women, transvaginal ultrasound can also be used as a way to confirm a pregnancy, especially in cases of early pregnancy, for example.
Exam price
The price of the transvaginal ultrasound examination can range from about 100 to 300 reais, depending on the region and clinic selected. However, during pregnancy and in other cases evaluated by the gynecologist, ultrasound can be done by the SUS at no cost.
How should the preparation
Usually no specific preparation is required, and it is only recommended to wear comfortable clothing that can be easily removed. In case the woman is menstruating or having bleeds outside the menstrual period, it is only recommended to remove the absorbent in case she is using.
In some exams, the doctor may ask to have ultrasound with a full bladder so as to move the intestine away and make it easier to obtain the images, so the exam technicians can offer 2 to 3 glasses of water about 1 hour before the examination. In these cases, it is only advisable not to use the bathroom until the examination.
How is the exam done?
The examination is done with the woman lying in a gynecological chair with legs open and slightly bent. During the examination, the doctor inserts the ultrasound device, which is protected with a condom and a lubricant, into the vaginal canal and let it stay for 10 to 15 minutes, and you can move it a few times for better images.
During this part of the examination you may feel a slight pressure in the belly or inside the vagina, but you should not feel pain. If this happens, it is important to inform the gynecologist to interrupt the exam or adjust the technique used.