The alkaline phosphatase test is usually used to look for diseases in the liver or bones when signs and symptoms such as abdominal pain, dark urine, jaundice or bone deformities and pain are present. It can also be performed as a routine examination, along with other tests, to assess the health of the liver.
Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme that is present in various tissues of the body, being in greater quantity in the cells of the bile ducts, which are channels that lead bile from the interior of the liver to the intestine, digestion of fats, and in the bones, being produced by the cells involved in its formation and maintenance.
Although in lower amounts, alkaline phosphatase is also present in the placenta, kidney and intestine and may therefore be elevated in pregnancy or in cases of renal insufficiency.
What is it for
The alkaline phosphatase test is used to investigate hepatic or bone disorders and its outcome may identify:
1. High alkaline phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatase may be elevated when there are liver problems such as:
Obstruction of the biliary flow, caused by gallstones or cancer, that block the channels that lead to bile into the intestine;
Hepatitis, which is an inflammation in the liver that can be caused by bacteria, viruses or toxic products;
Cirrhosis, which is a disease that leads to the destruction of the liver;
Consumption of fatty foods;
Renal insufficiency.
In addition, this enzyme may be very high in situations where there is an increase in bone formation activity, as in some bone cancers or in people with Paget's disease, which is characterized by the abnormal growth of certain parts of bones. Learn more about Paget's disease.
Mild changes may also occur during periods of healing of fractures, pregnancy, AIDS, intestinal infections, hyperthyroidism, Hodgkin's lymphoma, or even after a high-fat meal.
2. Low alkaline phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatase levels are rarely low, however this enzyme may be decreased in the following situations:
Hypophosphatasia, which is a genetic disease that causes deformations and fractures in the bones;
Malnutrition;
Magnesium deficiency;
Hypothyroidism;
Severe diarrhea;
Severe anemia.
In addition, some remedies such as the contraceptive pill and hormone replacement therapy remedies used in menopause may also cause a slight decrease in alkaline phosphatase levels.
When to take the exam
Examination of alkaline phosphatase should be done when signs and symptoms of liver disorders such as enlarged abdomen, pain in the right side of the abdomen, jaundice, dark urine, light stools and generalized itching are present.
In addition, this test is also indicated for people who have signs and symptoms at the level of bones such as generalized bone pain, bone deformities or fractures.

How is the exam done?
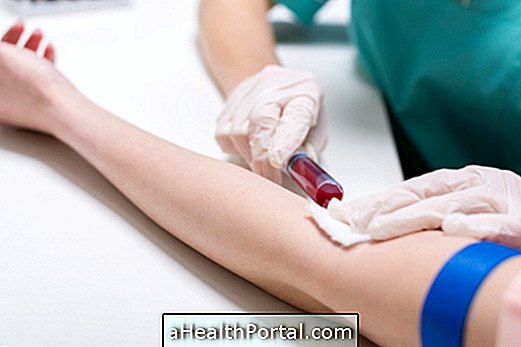
The test can be done in a laboratory where a health care professional removes about 5 ml of a blood sample from an arm vein, which is placed in an enclosed container, for analysis.
Reference values
The reference values of the alkaline phosphatase test vary with age due to growth:
Children and adolescents:
- <2 years: 85 - 235 U / L
- 2 to 8 years: 65 - 210 U / L
- 9 to 15 years: 60 - 300 U / L
- 16 to 21 years: 30 - 200 U / L
Adults:
- 30 to 120 U / L
In pregnancy, blood alkaline phosphatase levels may be slightly altered, due to the growth of the baby and because this enzyme is also present in the placenta.
Along with this examination, other liver enzymes such as alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, gamma glutamyl transpeptidase and bilirubin, imaging tests or even a liver biopsy may also be tested. See how these exams are done.