Thrombosis is the formation of clots or thrombi within the blood vessels, preventing the flow of blood. Any surgery can increase the risk of developing thrombosis, since it is common to be kept in a long time both during and after the procedure, which impairs circulation.
Therefore, in order to avoid thrombosis after surgery, it is recommended to begin small walks shortly after the doctor's release, wear elastic stockings for about 10 days or until it is possible to walk again normally, to move the legs and feet while is lying down and taking anticoagulant medicines to prevent the formation of clots, such as Heparin.
Although it may occur after any surgery, the risk of thrombosis is greater in the postoperative of a complex surgery or that it takes more than 30 minutes, such as surgery of the chest, heart or abdomen, such as bariatric surgery, for example. In most cases, thrombi form in the first 48 hours until about 7 days after surgery, causing redness in the skin, heat and pain in the leg. Check out more symptoms to identify the most rapid thrombosis in Deep Vein Thrombosis.
What to do after surgery to prevent thrombosis

To prevent thrombosis after surgery, your doctor may indicate:
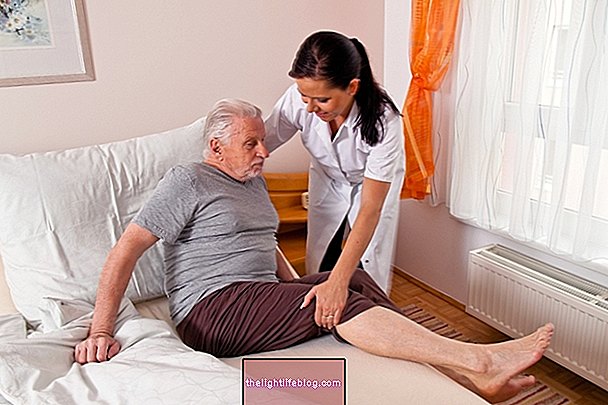
1. Walk as soon as possible
The operated patient should walk as soon as they have little pain and do not risk the scar breaking, as the movement stimulates blood circulation and decreases the risk of thrombi. Usually, the patient can walk at the end of 2 days, however it depends on the surgery and the orientation of the doctor.
2. Elastic stocking
The doctor may recommend the use of compression stockings even before surgery, which should be used for a period of about 10 to 20 days, until the movement of the body throughout the day returns to normal and is already possible to perform activities removed for body hygiene only.
The most commonly used half is the compression medium, which exerts a pressure of about 18-21 mmHg, which is able to compress the skin and stimulate the venous return, but the doctor may also indicate the high compression stockings with pressure between 20-30mmHg, in certain cases of greater risk, such as people with thick or advanced varicose veins, for example.
Elastic stockings are also advisable for anyone who has problems with venous circulation, people who are bedridden or have bed-restricted treatments, or who have neurological or orthopedic diseases that make movement difficult. Find out more details on what to wear and when to wear compression stockings.
3. Raise legs
This technique facilitates the return of the blood to the heart, which prevents the accumulation of blood in the legs and feet, in addition to decreasing the swelling of the legs.
When possible, the patient is instructed to move the feet and legs by bending and stretching about 3 times a day. These exercises can be guided by the physiotherapist still in the hospital.
4. Use anticoagulant medicines
Medications that help prevent the formation of clots or thrombi, such as injectable heparin, may be indicated by your doctor, especially when it is a time-consuming or long-term surgery, such as abdominal, thoracic or orthopedic.
The use of anticoagulant can be indicated until it is possible to walk and move the body normally. These medicines are also usually indicated during a hospital stay or during a treatment in which the person needs to be at rest or lying down for a long time. Understand the function of these drugs better in what they are anticoagulants and what they are for.
5. Massage your legs
Performing leg massage every 3 hours with almond oil or any other massage gel is also another technique that stimulates venous return and hinders blood clot formation.
In addition, there are other procedures that can be indicated by the doctor, such as electrical stimulation of calf muscles and intermittent external pneumatic compression, which is done with devices that stimulate blood movements mainly in people who can not do leg movements, as patients in coma.

Who is at increased risk of having a thrombosis after surgery
The risk of thrombosis after surgery is most when the patient is over 60 years of age, especially the elderly in bed after accidents or stroke, for example.
However, other factors that may increase the risk of having deep vein thrombosis after surgery are:
- Surgery done with general or epidural anesthesia;
- Obesity;
- Smoking;
- Use of contraceptive or other hormone replacement therapies;
- Having cancer or doing chemotherapy;
- Be a carrier of type A blood;
- Having heart disease, such as heart failure, varicose veins, or blood problems such as thrombophilia;
- Surgery done during pregnancy or soon after delivery;
- If there is a generalized infection during surgery.
When a thrombus develops due to surgery, there is a high chance of developing pulmonary embolism, because the clots decrease or block the passage of blood by lodging in the lungs, a situation that is serious and causes a risk of death.
In addition, there may also be swelling, varicose veins and brownish skin on the legs, which in more severe cases can lead to gangrene, which is the death of the cells due to lack of blood.