Melatonin is a hormone naturally produced by the body but it can be obtained in the form of a food supplement or medicine to improve the quality of sleep.
Although it is a substance that is also present in the body, taking medications or supplements containing melatonin may cause some side effects, which are rare but whose probability of occurring increases with the amount of melatonin that is ingested.

Most common side effects
Although rare, treatment with melatonin may cause the following side effects:
- Excessive fatigue and drowsiness;
- Lack of concentration;
- Aggravation of depression;
- Headache and migraine;
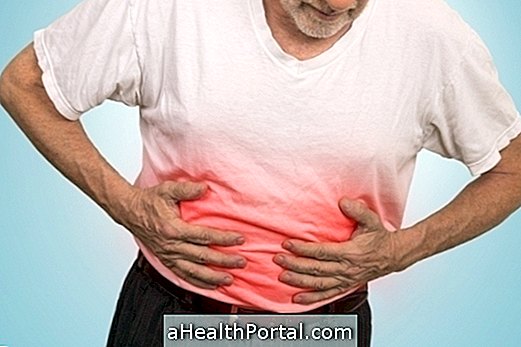
- Belly pain and diarrhea;
- Irritability, nervousness, anxiety and restlessness;
- Insomnia;
- Abnormal dreams;
- Dizziness;
- Hypertension;
- Heartburn;
- Canker sores and dry mouth;
- Hyperbilirubinemia;
- Dermatitis, rash and dry skin and generalized itching;
- Night sweats;
- Pain in chest and extremities;
- Symptoms of menopause;
- Presence of sugar and protein in the urine;
- Hepatic impairment;
- Weight gain.
The intensity of the side effects will depend on the amount of melatonin ingested, the higher the dose, the greater the risk of suffering from any of these side effects.
Contraindications of melatonin
Although it is a generally well tolerated substance, melatonin should not be used during pregnancy and breast-feeding or in people with allergies to any of the components of the tablets.
How to take melatonin
The recommended dose is 1 to 2 mg of melatonin once a day, about 1 to 2 hours before bedtime and after eating. A lower dose of 800 micrograms appears to be ineffective and doses greater than 5 mg should be used with caution.