The best treatment for obesity is with a diet to lose weight and regular exercise, but when this is not possible, there are drug options to help reduce appetite and binge eating, such as Sibutramine and Orlistat, or, ultimately, bariatric surgery, which decreases the area of food absorption by the gastrointestinal tract.
The first step, both to treat and prevent obesity, should always be control of calorie consumption, calculated according to the usual diet and the amount of weight to be lost, preferably with a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, fiber and water, as directed by the nutritionist. To find out what an ideal diet should look like, check out our fast and healthy weight loss diet.

However, in addition to diet and physical activity, other treatments for obesity that may be advised by an endocrinologist or nutrologist include:
1. Obesity Medications
The use of remedies to treat obesity are indicated in the following cases:
- BMI greater than 30 kg / m2;
- BMI greater than 27kg / m2, with other related diseases, such as diabetes, high cholesterol and high blood pressure;
- People with any type of obesity who can not lose weight with diet and exercise.
Medication treatment should be targeted to people who are involved in a lifestyle change program with dietary counseling and practice activities, otherwise it will not have a satisfactory effect.
The options for medicines to lose weight are:
| Types | Examples | How They Work | Side effects |
| Inhibitors of appetite | Sibutramine; Amfepramone; Femproporex. | They increase satiety and reduce hunger, which reduces calorie consumption throughout the day by increasing neurotransmitters such as norepinephrine, serotonin and dopamine. | Increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, dry mouth, headache and insomnia. |
| Absorption reducers in the gastrointestinal tract | Orlistat | They inhibit some enzymes in the stomach and intestines, which blocks the digestion and absorption of some of the fat from food. | Diarrhea, foul-smelling gases. |
| CB-1 receptor antagonist | Rimonabant | They block brain receptors to inhibit appetite, increase satiety and decrease food impulsivity. | Nausea, mood swings, irritability, anxiety, and dizziness. |
| Thermogenics | Ephedrine | Increase energy expenditure throughout the day. | Excessive sweating, increased heart rate, increased blood pressure. |
There are also medications used to treat other diseases that can help fight obesity, such as antidepressants, and some examples are Fluoxetine, Sertraline and Bupropion.
These drugs can only be used with strict medical guidance, preferably with experience in the use of these drugs, such as endocrinologists and nutrologists, due to the amount of side effects that require periodic attention and monitoring.
2. Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery is indicated in the following cases:
- Morbid obesity, with BMI greater than 40 kg / m2;
- Moderate obesity, with a BMI greater than 35mg / m2, associated with uncontrolled obesity diseases such as diabetes, sleep apnea, hypertension, high cholesterol, cardiovascular diseases, stroke, arrhythmias and osteoarthritis.
Some of the most commonly performed types of surgery are:
| Type | How is it done? |
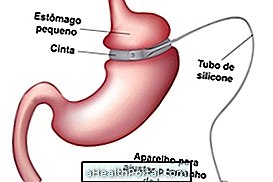
| Gastric band | An adjustable band is placed to decrease the diameter of the stomach. |
| Gastric Bypass | It causes the stomach to decrease with deviation from the remaining part to the intestine. |
| Biliopancreatic derivation | It also removes part of the stomach, creating another type of deviation to the intestine. |
| Vertical Gastrectomy | Much of the stomach responsible for absorption is withdrawn. |
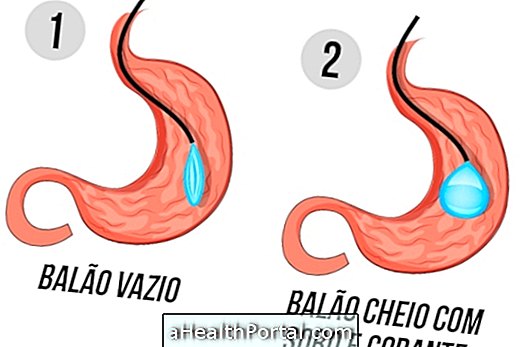
Another less invasive procedure option is the placement of a temporary intragastric balloon, indicated as an incentive for some people to reduce food consumption for a period.
The type of surgery indicated for each person is decided by the patient together with the gastric surgeon, who assesses the needs of each person and the procedure that may best suit. Understand better how it is done and how recovery from bariatric surgery is.
Tips for not giving up treatment
The treatment for obesity is not easy to fulfill because it implies changing the eating habits and lifestyles that the patient has done throughout life, so some tips to help not give up treatment can be:
- Set weekly goals that are achievable;
- Ask the nutritionist to adjust the diet if it is too difficult to meet;
- Choose a physical exercise you enjoy, and practice on a regular basis. Find out what the best weight-loss exercises are;
- Record the results by noting measurements on paper or with weekly photos.
In the following video, see important tips from the dietitian to make weight loss easier:

Another important direction to keep the focus of weight loss is to keep a monthly or quarterly follow up with the nutritionist and the doctor, so that any difficulty or change throughout the treatment is solved more easily.
It is important to remember that there are free weight loss programs, which are carried out by university hospitals with an endocrinology service in all states, and it is possible to inform about referrals and consultations at the health post.