Hepatitis E is a disease caused by the hepatitis E virus, also known as HE, which can enter the body through contact or consumption of contaminated food and water. This disease is often asymptomatic, especially in children, and is usually controlled by the body itself.
Because it is controlled by the immune system itself, hepatitis E does not have a specific treatment, and rest, fluid ingestion and greater attention to sanitation and hygiene conditions are recommended, especially with regard to food preparation.
Symptoms of hepatitis E
Hepatitis E is usually asymptomatic, especially in children; however, when symptoms appear, the main ones are:
- Skin and yellow eyes;
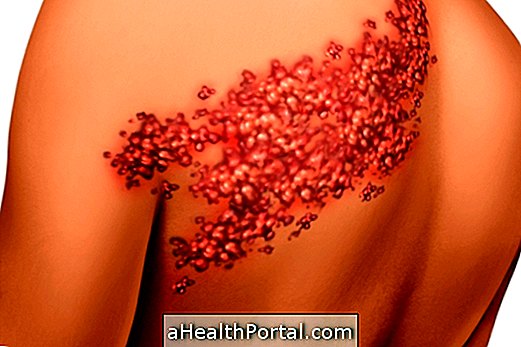
- Itching through the body;
- Clear stools;
- Dark urine;
- Low fever;
- Indisposition;
- Nipple;
- Abdominal pain;
- Vomiting;
- Lack of appetite;
- There may be diarrhea.
Symptoms usually appear between 15 and 40 days after contact with the virus. Diagnosis is made by screening antibodies against the hepatitis E virus (anti-HEV) in a blood sample or by screening for viral particles in the faeces.
Hepatitis E in pregnancy
Hepatitis E in pregnancy can be quite serious, especially if the woman has contact with the hepatitis E virus in the third trimester of pregnancy because it increases the risk of fulminant hepatitis and is associated with a higher mortality rate. In addition, it can result in premature labor. Understand fulminant hepatitis and how treatment is done.
How Transmission Happens
The transmission of hepatitis E virus occurs via fecal-oral, mainly by the contact or consumption of water and foods contaminated by urine or feces of contaminated persons.
The virus can also be transmitted through direct contact with infected people, but this mode of transmission is rarer.
How treatment is done and how to prevent it
Hepatitis E is self-limited, that is, it is resolved by the body itself, requiring only rest, good nutrition and hydration. In addition, if the person is taking immunosuppressive drugs, it is recommended to suspend until the disease is resolved, because the hepatitis E virus is controlled by the immune system. If necessary, the doctor may choose to treat the symptoms presented by the person.
In more severe cases, especially when there is co-infection with the hepatitis C or A virus, the use of antiretroviral drugs, such as Ribavirin, for example, may be indicated but it should not be used by pregnant women. Learn more about Ribavirin.
There is no vaccine for hepatitis E, since it is a benign, self-limited and rare prognosis disease in Brazil. Thus, the best way to prevent hepatitis E virus infection is through hygiene measures such as washing your hands after going to the bathroom and before eating, and only use filtered water to drink, prepare or cook food .