Typhoid fever is an infectious disease that can be transmitted through the consumption of water and food contaminated with Salmonella typhi, which is the etiological agent of typhoid, causing symptoms such as high fever, poor appetite, enlarged spleen, and red skin patches, for example.
The treatment of typhoid fever can be done with antibiotics, resting and ingestion of fluids to hydrate the patient. The vaccine against typhoid fever is the best way to prevent the disease and is indicated for individuals who live or are going to travel to the regions where the disease is frequent.
Typhoid fever is associated with low socioeconomic levels, mainly due to poor sanitation, personal and environmental hygiene, and typhoid fever in Brazil is more frequent in states where conditions are more precarious.
Typhoid fever and paratyphoid are similar diseases with the same symptoms and treatment; however, paratyphoid fever is caused by the bacterium Salmonella paratyphi A, B or C and is usually less severe.
Typhoid fever and typhus are different diseases, as typhus is an infectious disease caused by the Rickettsia bacterium, which is transmitted through the bite of an infected insect such as lice, fleas or ticks or contamination by the feces of an infected insect.
Images of typhoid fever
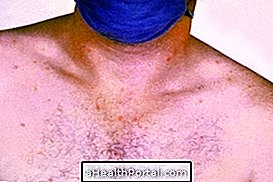

Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Harrison Internal Medicine, 2013
The images show one of the characteristic symptoms of typhoid fever, the red patches on the chest and abdomen.
Symptoms of Typhoid Fever
Symptoms of typhoid fever include:
- High fever;
- Vomiting;
- Bellyache;
- Constipation or diarrhea;
- Headaches;
- Spleen enlargement;
- Loss of appetite;
- Weight loss;
- Depression;
- Cough;
- Reddish red skin;
- Swollen belly.
The symptoms of typhoid fever may in some cases resemble respiratory tract infections and meningitis. The incubation period of the disease is 1 to 3 weeks.
The diagnosis of typhoid fever can be made through examination of blood and faeces.
Vaccine for typhoid fever
The typhoid vaccine is the most effective option to prevent typhoid fever. It is indicated for individuals who inhabit or are going to travel to the regions where the disease is frequent.
Given that the vaccine does not fully protect the individual from typhoid fever, it is important to take other measures to prevent typhoid fever, such as before drinking, boiling or filtering water, using mineral water to even brush teeth, daily hygiene, avoiding poor hygiene, washing hands before preparing food and after going to the bathroom and having basic sanitation.
Transmission of typhoid fever
The transmission of typhoid fever is usually through the ingestion of water and food, which have been contaminated with feces or urine of a sick individual or an individual who despite not showing symptoms can still be carriers of the bacteria, such as, vegetables that have been washed with contaminated water or undercooked or raw foods.
Another form of typhoid contagion is through the hand, which although it occurs more rarely, can happen when the individual brings to the mouth a hand that came into contact with the dirty hand of the sick person or carrier of the bacteria that causes typhoid fever. In addition, typhoid fever can also be transmitted through anal sex.
How To Treat Typhoid Fever
The treatment of typhoid fever can be done with the administration of antibiotics, rest, diet low in calories and fats and intake of liquids for the patient to stay hydrated.
In more severe cases, it may be necessary for the individual to be hospitalized for surveillance and serum and antibiotics for the vein.
After treatment, the individual may no longer have symptoms but still contain the bacteria of typhoid fever in the body, so it is important to take blood to confirm the presence or not of the bacteria and continue with the treatment until it is completely eliminated.
Untreated typhoid fever can lead to serious complications for the individual, such as bleeding, perforation of the intestine, general infection, coma, and even death.
Useful links:
- Cholera
- Salmonellosis
- Leptospirosis