After a sexual intercourse without a condom, you should take a pregnancy test and go to the doctor to see if you have been infected with any sexually transmitted disease such as gonorrhea, syphilis or HIV.
These precautions are also important when the condom is punctured, it has been misplaced, when it was not possible to maintain the condom during all intimate contact and also in case of interrupted intercourse because in these situations there is also the risk of pregnancy and transmission of diseases.

What to do to avoid pregnancy
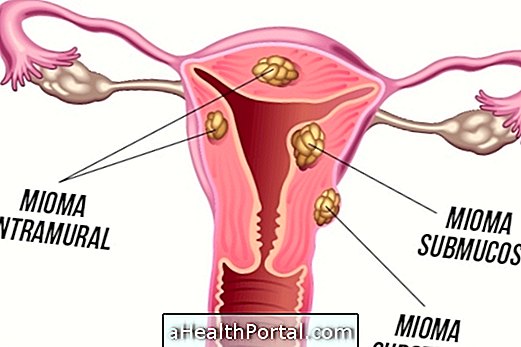
There is a risk of getting pregnant after having sex without a condom when the woman does not use an oral contraceptive or has forgotten to take the pill on any of the days prior to intimate contact.
So in these cases, the woman can take the morning- after pill up to 72 hours after intercourse to avoid unwanted pregnancy. However, the morning-after pill should never be used as a contraceptive method because its efficacy decreases with each use. What you may feel after taking this medicine: Side effects of the morning after pill.
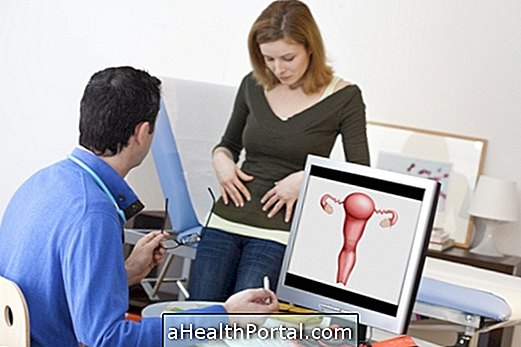
If there is delayed menstruation, even after taking the morning-after pill, the woman should take a pregnancy test after the first day of the delay to confirm whether or not she is pregnant, since there is a possibility that the morning-after pill will not have produced the expected effect. See what are the first 10 symptoms of pregnancy.
What to do if you suspect STDs
The greatest risk after intimate contact without a condom is to be infected with sexually transmitted diseases. So if you have symptoms such as:
- Itching,
- Redness or
- Intimate discharge
It is advised to consult the doctor within the first few days after the relationship to diagnose the problem and initiate appropriate treatment.
Even if you do not have symptoms, you should go to the doctor to be examined and know if you have any changes in your intimate area. If you can not in the first days after the relationship, you should go as soon as possible because the sooner you start treatment, the faster the cure. Get to know the symptoms and treatments of the most common Sexually Transmitted Diseases.
What to do in case of suspected HIV
If the sexual relationship has occurred with an HIV-infected patient, or if you do not know if the person has HIV, the risk of having the disease is greater, and so you can ask the infectologist to take a prophylactic dose of HIV, up to 72 hours, which decreases the risk of developing AIDS.
However, this prophylactic dose is usually only available to health care professionals who become infected with infected needles or to victims of rape, and in the latter case it is important to go to the emergency room to collect traces that help identify the offender.
Thus, if AIDS is suspected, a rapid HIV test should be conducted at AIDS testing and counseling centers in the country's large capitals.
See too:
- Quick test identifies HIV in saliva and blood
- Understanding the HIV Test Outcome