The diagnosis of a nodule in the lung is not the same as cancer, since in most cases the nodules are benign and, therefore, do not put their lives at risk, especially when they are smaller than 30 mm.
However, in rare cases, the presence of a nodule may be an early sign of lung cancer or elsewhere in the body, and therefore it is important to maintain a regular assessment with imaging tests to evaluate growth and initiate treatment if necessary.
How to know if the lump is cancer
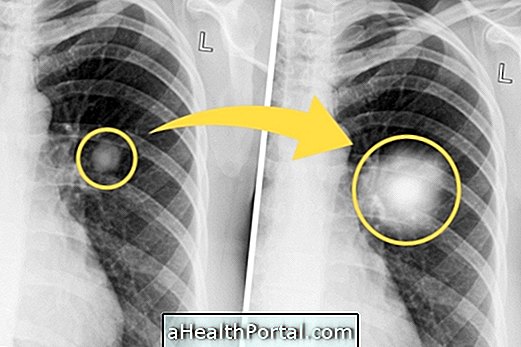
To find out if a lump is malignant, the pulmonologist usually asks for another imaging test, such as a CT scan, and about 4 months later, repeat the test to see if the lump has grown or changed shape and appearance.
Usually, benign nodules remain the same size and do not change much, while cancer nodules increase in size to almost double and greatly alter their shape, showing an irregular mass rather than a round mass that is characteristic of the benign pulmonary nodule .
What can cause a lump
The causes of nodules in the lung vary according to their type:
- Benign nodule: usually is a result of scars in the lung caused by previous infections, such as pneumonia, or as a result of tuberculosis, for example;
- Malignant nodule: It has the same causes of lung cancer and is therefore more common in smokers and in people who are frequently exposed to cigarette smoke.
In addition, the malignant lump can also be caused by cancer elsewhere in the body, such as the stomach or intestine, and it is recommended to do other tests, such as colonoscopy or endoscopy, when there is a suspicion of cancer in these organs.
Symptoms of malignant nodule
Nodules in the lung rarely cause any kind of symptom, whether malignant or benign, so it is common to find them only during routine exams such as X-rays or CT scans.
However, some symptoms that may alert you to changes in the lungs, such as lumps, that should be evaluated by a pulmonologist include difficulty breathing, easy tiredness, chest pain, and a feeling of shortness of breath.
How is nodule treatment done?
The treatment varies according to the type, and in the case of the benign nodule, usually no treatment is recommended, only a constant evaluation with 1 X-ray per year to ensure that the nodule does not change.
In the case of a malignant nodule, the pulmonologist usually advises to perform surgery to remove the nodule. Thus, depending on the size of the nodule the surgery can be done by laparoscopy, through small cuts in the belly, or with a large cut, to remove all the affected lung tissue.
When the treatment is not done properly the malignant lump may become cancer, know the specific treatment in these cases.