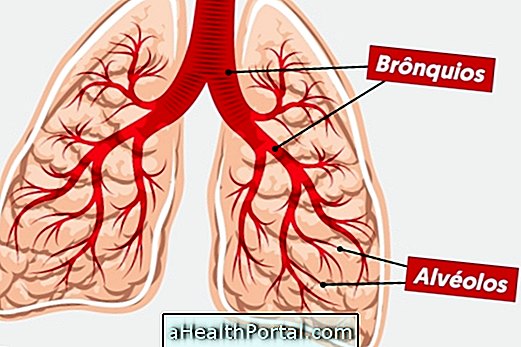
Pulmonary bronchiectasis is a disease characterized by permanent dilation of the bronchi, which can be caused by recurrent bacterial infections or due to obstruction of the bronchi. This disease has no cure and is usually associated with other conditions such as cystic fibrosis, pulmonary emphysema and immobile eyelash syndrome, also known as Kartagener Syndrome. Learn more about this syndrome.
Treatment of bronchiectasis is done with the use of medications to decrease symptoms and prevent disease progression and respiratory physiotherapy to facilitate breathing.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment for bronchiectasis is done with the aim of improving the symptoms and preventing the progression of the disease, since this condition has no cure. Thus, the use of antibiotics may be recommended by the physician to treat infections, mucolytics, to facilitate the release of mucus, or bronchodilators, to facilitate respiration.
In addition, respiratory physiotherapy is very important for improving the person, because through physical therapy it is possible to remove mucus from the lungs and increase gas exchange, facilitating breathing. Understand how respiratory physiotherapy works.
In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove part of the lung.
Symptoms of Pulmonary Bronchiectasis
Pulmonary bronchiectasis may be characterized by the following symptoms:
- Persistent cough with catarrh;
- Shortness of breath;
- Loss of appetite;
- General malaise;
- There may be a cough with blood;
- Chest pain;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Bad breath;
- Fatigue.
To diagnose bronchiectasis, the physician evaluates the symptoms and requests laboratory tests, such as sputum analysis, to identify a possible infection, and imaging tests, such as computed tomography and X-ray, in which bronchial characteristics are observed. usually increased in this condition.
In addition, the physician may request a spirometry, which evaluates lung function by measuring the amount of air entering and exiting the lung, and a bronchoscopy, which is an imaging examination to visualize the airways, including larynx and trachea. Understand what bronchoscopy is and how it is done.
Main causes
Pulmonary bronchiectasis can be caused by several situations, such as:
- Severe or recurrent lung infections;
- Pneumonia;
- Problems in the immune system;
- Impaired eyelash syndrome;
- Sjögren's Syndrome;
- Pulmonary emphysema - understand what it is, symptoms and how to treat pulmonary emphysema;
- Bronchial asthma;
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
If the cause is not identified and treatment initiated, bronchiectasis can cause several complications, such as respiratory failure and pulmonary collapse (or atelectasis), for example, a respiratory complication characterized by collapse of the pulmonary alveoli that prevents sufficient passage of air. Learn more about pulmonary atelectasis.