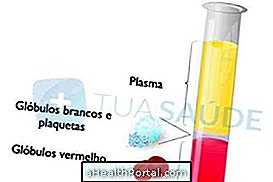
Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, are blood cells produced by the bone marrow and are responsible for the blood coagulation process, with increased platelet production when bleeding, for example, prevents excessive blood loss.
The platelet reference value is between 150, 000 and 450, 000 platelets / μL of blood, however some conditions may interfere with the platelet production process, with increasing or decreasing blood concentrations, which is called thrombocytopenia.
Not only is platelet counts important, but so is the quality of platelets produced by the bone marrow. Some diseases related to platelet quality are Von Willebrand's disease, which is related to the coagulation process, Scott's Syndrome, Glanzmann's Thrombasthenia, and Bernard-Soulier's Syndrome. In addition, it is important to be aware of hemoglobin values, which can indicate diseases such as anemia, leukemia and pulmonary emphysema.
High platelets
The increase in the number of platelets, also called platelets or thrombocytosis, can occur due to pathological or physiological causes, with intense exercise, labor, high altitude, smoking, stress or use of adrenaline, for example.
The main pathological causes of thrombocytosis are:
- Severe hemolytic anemia;
- Iron deficiency anemia;
- Myeloproliferative Syndromes, such as Essential Thrombocythemia, Polycythemia Vera and Myelofibrosis;
- Sarcoidosis;
- Acute and chronic infections;
- Leukemia;
- After acute hemorrhage;
- After removal of the spleen, known as splenectomy;
- Neoplasms;
- Ulcerative colitis;
- After operations.
It is important that the cause of platelet augmentation is identified so that the doctor can indicate the best treatment option.
In addition to thrombocytosis, another platelet-related disorder is thrombocytopenia, which corresponds to decreased platelets in the blood, which may occur due to the use of some medications, pernicious anemia, autoimmune diseases such as lupus, and nutritional deficiencies, for example. Know other causes of thrombocytopenia and how to treat it.
How to identify
Usually the increase in the number of platelets does not cause symptoms, being perceived from the accomplishment of the hemogram, which is the blood test that evaluates the quantity and characteristics of the blood cells.
In some cases there may be the appearance of symptoms, and may vary according to the cause, being the main nausea, vomiting, dizziness and tingling of the extremities.
How to Lower High Platelets
According to the blood platelet concentration, presence of symptoms and general condition of the person, the general practitioner or hematologist may recommend the use of acetylsalicylic acid in order to reduce the risk of thrombosis, or hydroxyurea, which is a medicine capable to decrease the production of blood cells through the bone marrow.
In addition, if the platelet concentration is too high to the point of putting the patient's life at risk due to the high chance of clot formation, therapeutic thrombocytophoretic therapy may be recommended, which is a procedure by which aid of an equipment, the excess of platelets, and, therefore, able to balance the circulating platelet values.