Pyoderma is a skin infection caused by bacteria that may have pus, or not. These lesions are mainly caused by S. aureus and S. pyogenes and cause lesions on the skin that form crusts, blisters, and are well delimited or extensive, and therefore should always be observed by the physician for treatment to be started as soon as possible.
When treating this type of skin lesion is not done with the correct antibiotics the lesions can worsen and reach the bloodstream spreading throughout the body, which is very serious. Thus, whenever a skin itchy, it hurts, the area becomes reddish and crusts, blisters or peeling appear, you should get medical help as soon as possible.
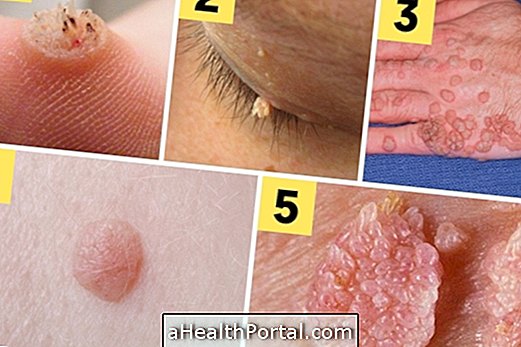
Some examples of bacterial skin infections are:
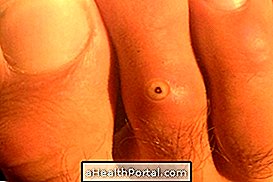
1. Boil
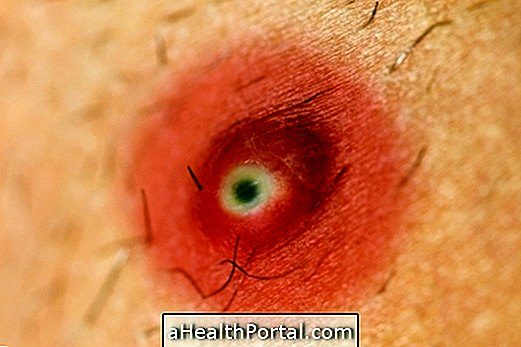
The boil is a very sore, rounded lesion that can appear anywhere on the body, the region also shows itching, malaise and low fever.
- How to treat: Antibiotic ointments such as Furacin, Nebacetin or Trok G should be indicated, for example under medical indication. Learn more names of pomades for boils.
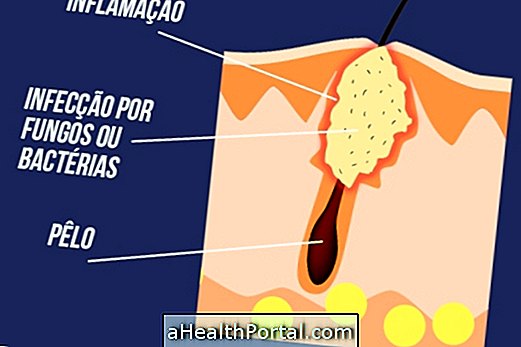
2. Folliculitis

Folliculitis is a very common skin infection due to obstruction of the hair follicle by one ingrown hairs, but when it becomes deep it can become a furuncle with pus formation.
- How to treat: Usually in milder cases exfoliate the skin with exfoliating products is enough to unclog the follicle, but if there are signs of inflammation such as intense redness and swelling you should go to the doctor because it can also become a boil, an antibiotic ointment, and in the most severe cases in the larger lesions, taking antibiotics may also be recommended. Learn how to treat folliculitis so that it does not become a boil.
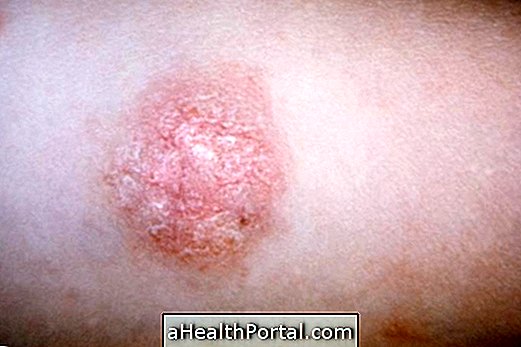
3. Erysipelas

In the case of erysipelas besides extensive redness in a region of the skin, there are also other symptoms such as headache, fever and pain in the joints. The most affected areas are the extremities of the skin and face, and in some cases blisters may form on the skin.
- How to treat: Rest is recommended, taking analgesics and antibiotics like penicillin or procaine. When erysipelas is not serious treatment can be done at home, but there are situations where hospital admission is required with antibiotic application directly into the vein. Learn more about the treatment of erysipelas.
4. Infectious cellulitis

Infectious cellulitis is a skin disease caused by scoliosis that affect the deeper layers of the skin causing symptoms such as intense redness, swelling, very hot skin and a high fever.
- How to treat: Antibiotic medicines such as Amoxicillin or Cephalexin should be used for 10 to 21 days. In the most severe cases the infection can spread throughout the body, requiring hospital admission. Learn more details of infectious cellulite treatment.
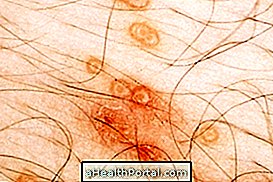
5. Impetigo

Impetigo is caused by staphylococcus or streptococcus, being more common in children, and may present with or without blisters. The most common is to affect the region of the mouth and nose forming dry crusts of honey color.
- How to treat: Your doctor may advise you to use saline to soften the scabs and then apply an antibiotic ointment such as neomycin, nebacetin, mupirocin, gentamicin, retapamiline or cicatrene for 5 to 7 days until the wounds have completely healed. See more care needed to cure impetigo.
6. Ectima

The ecthyma is very similar to impetigo, but it affects the deeper layers of the skin and can leave scars, most commonly occurring as a complication of poorly treated impetigo.
- How to treat: In addition to keeping the area clean and dry, using saline and antiseptic lotion, antibiotics should be used as an ointment, as indicated by your doctor, and if there are no signs of improvement in 3 days, your doctor may recommend taking antibiotics. Learn more details of ecthyma treatment.
7. Scalded skin syndrome
This skin disease is more common in children who get their skin greatly affected, with large areas of flaking, fever, chills and weakness.
- How to treat: The use of antibiotics by the vein is essential and then in the form of tablets or syrups, and moisturizing creams to protect the skin.
Possible Complications
Bacterial infections in the skin can become severe, spreading over larger areas, and even reach the bloodstream, which is very serious. However, this only happens when the use of antibiotics starts too late, when the person does not use antibiotics properly, or when the antibiotic recommended by the doctor is not the most appropriate for each type of infection.
To avoid this type of complication it is recommended:
- Go to the doctor as soon as you notice any changes in the skin;
- Use the antibiotic prescribed by the doctor, respecting the doses, times and number of days;
- After starting medicines, if there are no signs of improvement within 3 days, you should see your doctor, especially if there are signs of worsening.
Signs of improvement are decreased symptoms, redness, normalization of temperature, and better appearance of wounds. On the other hand, the signs of worsening are when the lesions appear to be bigger and worse, other symptoms such as fever, increased blisters or pus, which initially were not present in the medical evaluation, appear.









.jpg)