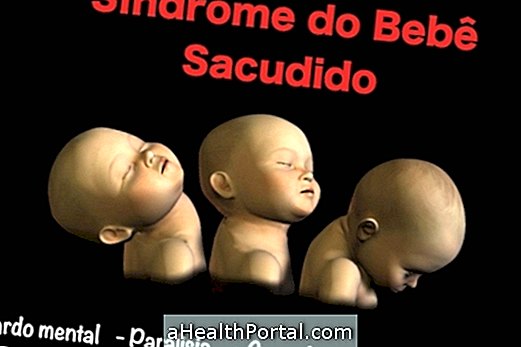
Shaken Baby Syndrome can occur when adults make jerky movements in children under 2 years of age, such as swinging them back and forth with force and without supporting the head or making jokes involving throwing the child up.
These sudden movements can cause bleeding and lack of oxygen in the baby's brain, as they still have weak neck muscles, not having the strength to hold their head properly.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the syndrome are difficult to identify because babies can not express what they feel, but problems usually arise such as:
- Excessive irritability;
- Dizziness and difficulty standing up;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Lack of appetite;
- Tremors;
- Vomiting;
- Pale or bluish skin;
- Headache;
- Difficulties to see;
- Convulsions.
Thus, one must be alert to signs such as irritation, constant crying, drowsiness, vomiting and the presence of bruises on the baby's body.
In addition, it is important to remember that the symptoms do not usually arise soon after the sudden jerk in the child, but appear a few hours or days after the aggression.
Consequences
The child's brain is still very sensitive up to 2 years of age, but the worst sequelae occur mainly in infants under 6 months of age or suffering from maltreatment. Developmental delays, mental retardation, paralysis, loss of vision, hearing, convulsions, coma and death.
In most cases, this syndrome occurs in unstable families with stressed parents who do not deal well with the baby's arrival or with a history of alcoholism, depression or family mistreatment.
What to do
You should watch for signs of changes in your baby's behavior and take it to your doctor if you experience any symptoms of Shaken Baby Syndrome for further tests such as blood tests, X-rays, or CT scans that check for changes in the brain.
In addition, it should be noted if the child is afraid of a relative or caregiver, who may be the source of abuse or abusive play.
It is also important to remember that packing the baby in the arms, swinging the baby on the lap and holding the head or use the cart to carry it, even on terrain that causes bumping, are not causes of health risk for the child.
How to treat
Treatment is done according to the sequelae and lesions caused by the syndrome in the baby, and may require the use of medications, psychotherapy or surgeries to repair the damage.
In addition, it is important that parents and caregivers also seek help with a psychotherapist to help control stress and anger, and learn to deal with calm and patience with the child.
To know how to control your baby's crying, see:
- 6 Ways to Make Baby Stop Crying
- 10 Causes of Baby Crying











.jpg)