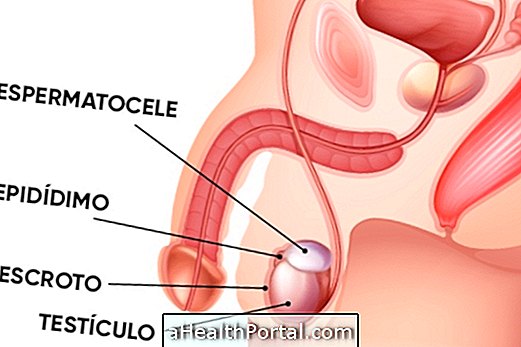
Spermatocele, also known as a seminal cyst or epididymal cyst, is a small sac that develops in the epididymis, which is where the sperm-carrying canal connects to the testis. In this bag there is accumulation of small amounts of spermatozoa and, therefore, may indicate an obstruction in one of the channels, although it is not always possible to identify the cause.
In most cases, the spermatocele does not cause any type of pain, being only identified with the palpation of the testicles during the bath, for example.
Although it is almost always benign, this change must always be evaluated by a urologist, since this type of alteration can also be a sign of a malignant tumor, even in rare cases. Normally, spermatocele does not reduce the fertility of the man and, therefore, also may not need treatment.
Main symptoms
The main sign of spermatocele is the appearance of a small lump near the testicle, which can be moved but does not hurt. However, if you continue to grow over time, you may begin to produce other symptoms such as:
- Pain or discomfort on the side of the affected testicle;
- Feeling of weight in the intima;
- Presence of large lump near the testicle.
When any change in the testicle is identified, even if there are no other symptoms, it is very important to consult a urologist to look for other more serious causes, such as torsion of the testicle or even cancer, for example.
How is the treatment done?
Since most spermatoceles do not cause any type of complication or discomfort, usually no treatment is required. However, the urologist can schedule frequent consultations about 2 times a year to assess the size of the cyst and ensure that it is not suffering from changes that may indicate malignancy.
If the spermatocele causes discomfort or pain during the day to day the doctor can prescribe the use of medicines to diminish the inflammation, like Ibuprofen or Acetominofeno. After using these remedies for 1 or 2 weeks, the symptoms may disappear completely, and if this does not require further treatment. However, if symptoms persist, it may even be recommended to undergo minor surgery.
Surgery for spermatocele
Surgery to treat a spermatocele, also known as spermatoceloctomy, is usually done under general anesthesia and is used for the physician to separate and remove the spermatocele from the epididymis. After surgery, it is usually necessary to wear underwear made of bandages that helps keep the pressure in place, preventing the cut from opening when moving, for example.
During recovery it is still recommended to have some care such as:
- Apply ice packs to the intima;
- Take medications prescribed by your doctor;
- Avoid wetting the intimate region until the stitches are removed;
- Do the wound treatment at the health post or hospital.
Although rare, some complications may occur after surgery, especially infertility if there is any lesion in the epididymis. Therefore, it is very important to select a certified urology clinic with a medical surgeon with plenty of experience.