The human papillomavirus, also known as HPV, is a virus that infects the skin and mucous membranes in men and women. There are more than 120 different types of HPV, of which 40 affect the genital organs preferentially, being types 16 and 18 high risk, accounting for 75% of the most serious lesions, such as cancer.
HPV usually has no symptoms, however, some types can cause various diseases like genital warts, cervical cancer, vagina, vulva, anus and penis. In addition, they can also cause tumors inside the mouth and throat.
1. HPV has a cure
TRUTH. Usually, HPV infections are controlled by the immune system and the virus is usually eliminated by the body. However, as long as the virus is not eliminated, even in the absence of symptoms, there may be the risk of infecting other people. See when HPV cures alone when spontaneous HPV remission occurs.
However, it is important that any HPV lesions are regularly evaluated by your doctor to treat and prevent more serious diseases. One should also strengthen the immune system with supplements of Vitamin C, Zinc.
2. HPV is a sexually transmitted disease
TRUTH. HPV can be transmitted very easily during any kind of sexual, genital or oral contact, so it is very important to use a condom. Learn more about how HPV is caught.
3. The use of a condom prevents the transmission of HPV
MYTH. Condom use can prevent about 70% to 80% of HPV infection, but its use is recommended because it reduces the risk of infection and can also prevent other diseases such as AIDS, some types of hepatitis and syphilis.
4. HPV can pick up through towels, underwear or toilet bowl
TRUTH. Although much rarer than direct contact in sexual intercourse, contamination by objects can also happen, especially those that come in contact with the skin. Therefore, you should avoid sharing towels, underwear and be careful when using the toilet. Here's how to use the bathroom so you do not get sick.
5. HPV usually has no symptoms
TRUTH. People may be carriers of the virus and do not have any symptoms, so most women find that they have this virus only on the pap smear, so it is very important to do this test regularly. See what this exam consists of.

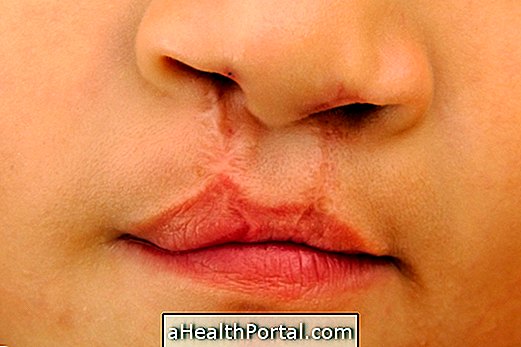
6. Genital warts may disappear without treatment
TRUTH. The warts can disappear naturally, without any kind of treatment. However, depending on the size and location, there are several ways to treat, with applying a cream or a solution that removes them slowly, by freezing, cauterization or laser, or even through surgery.
In some cases the warts may reappear even after treatment. Check out how to treat genital warts.
7. The HPV vaccine protects against all diseases caused by the virus
MYTH. Vaccines that are available only protect against the most frequent types of HPV, so if the infection is caused by another type of virus, it could give rise to a disease. Thus, it is very important to take other preventive measures such as condom use, and in the case of women, do the pap smear for cervical cancer screening. Learn more about the HPV vaccine.

8. Genital warts appear very often
TRUTH. One in 10 people, male or female, will have genital warts throughout their lives, and may appear weeks or months after sexual contact with infected persons. Here's how to identify genital warts.
9. HPV does not cause disease in humans
MYTH. As with women, genital warts may also appear in men infected with HPV. In addition, the virus can still cause cancer of the penis and anus. See more on how to identify and treat HPV in men.
10. All women infected with HPV have cancer
MYTH. In most cases the immune system eliminates the virus, however, some types of HPV can lead to the formation of genital warts or benign changes in the cervix. Therefore, it is very important to strengthen the immune system, feeding well, sleeping well and doing physical exercises.
If these abnormal cells are not treated, they can cause cancer and can take several years to develop, so early detection is very important.