The treatment of human visceral leishmaniasis, also known as kalazar, is mainly done with Pentavalent Antimony Compounds, for 20 to 30 days, in order to eliminate the microorganism that causes the disease.
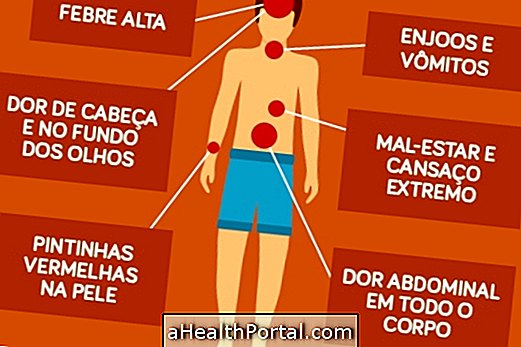
Visceral leishmaniasis is an infection caused in Brazil by the protozoan Leishmania chagasi, transmitted by mosquitoes of the species L. longipalpis and L. cruzi, a disease that worsens slowly and can become severe, therefore, in the presence of signs and symptoms that indicate this disease, it is important to seek medical attention for the correct diagnosis and treatment. Learn more about how to identify visceral leishmaniasis.
In addition to the drugs to eliminate the protozoan, the treatment should involve the control of common complications of this disease, such as anemia, diarrhea, malnutrition, bleeding and infections due to immunity, because these are debilitating and life-threatening situations.
Most Used Remedies
Pentavalent Antimony Compounds, such as Meglumine Antimonate and Sodium Stibogluconate, are the main drugs used to treat shingles, which are the main treatment option, applied in intramuscular or venous doses, for 20 to 30 days. Learn more about how it is used and the price of the medicine most used in the treatment of Leishmaniasis.
In a few cases, these medications can cause side effects such as arrhythmias, body aches and poor appetite, and are contraindicated in people with impaired renal or hepatic function in pregnant women in the first two trimesters of pregnancy and in cases with signs alterations in electrocardiogram, known as QT interval increase.
Other alternative options in cases of lack or contraindications to these remedies are liposomal Amphotericin B, amphotericin B colloidal dispersion, Pentamidines and immunomodulators such as interferon gamma and GM-CSF.
Care during treatment
Before starting treatment, some care should be taken, including the evaluation and stabilization of clinical conditions caused by the disease, such as dressings or transfusions for bleeding controls, replacement of iron and vitamins or, if necessary, blood transfusion, to assist in the recovery of anemia, diet with proteins and calories to improve malnutrition and use of antibiotics to treat infections.
Treatment can be done at home provided that the person is able to receive the necessary care at this location and is able to go to the hospital to receive the medications and medical reassessments. In addition, hospital admission should be recommended whenever there is:
- Severe anemia, with hemoglobin less than 5g%;
- Severe or prolonged diarrhea;
- Severe malnutrition;
- Presence of bleeding;
- Generalized swelling;
- Presence of other associated diseases, such as arterial hypertension, heart disease, nephropathy or liver disease;
- Children younger than 6 months or elderly over 65 years of age;
- Improvement delay or when disease returns after treatment is finished.
In addition, after completion of treatment, the person should be followed up at doctor's office after 3, 6 and 12 months, and if he remains stable on the last evaluation, the patient is considered cured.

Signs of improvement
Signs of improvement may already occur after the first week after the start of treatment and are characterized by decreased fever, reduced belly swelling, weight gain and recovery of the disposition.
Signs of worsening
These signs are most common when treatment is not started quickly and include increased or re-emergence of fever, weight loss, constant weakness, viral and bacterial infections by the body and bleeding.