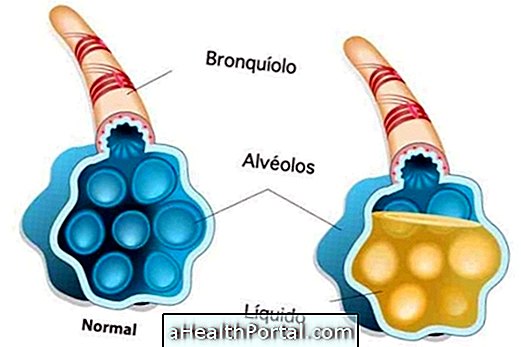
Treatment of viral pneumonia can be done at home for 5 to 10 days and ideally should be started within 48 hours of the onset of symptoms.
If there is suspicion of viral pneumonia or a picture of influenza caused by viruses at higher risk of causing pneumonia, such as H1N1 or H5N1, in addition to measures such as rest and hydration, antiviral medicines Oseltamivir or Zanamivir are used, for example, to help eliminate viruses and prevent complications.
Other medications, such as corticosteroids, such as Prednisone, decongestants such as Ambroxol, and painkillers such as Dipyrone or Paracetamol, are used throughout the treatment to relieve symptoms such as accumulation of secretions and pain in the body, for example.

Remedies to treat viral pneumonia
Treatment of viral pneumonia or any suspected H1N1 or H5N1 virus infection involves the use of antiviral drugs prescribed by the general practitioner or pulmonologist, such as:
- Oseltamivir, known as Tamiflu, for 5 to 10 days, usually when caused by the Influenza virus, such as H1N1 and H5N1;
- Zanamivir, for 5 to 10 days, also when there is suspicion of infection by the virus Influenza, like H1N1 and H5N1;
- Amantadine or Rimantadine are also antivirals useful in the treatment of Influenza, although they are less urated because some viruses may be resistant to them;
- Ribavirin for about 10 days in the case of pneumonia caused by other viruses, such as respiratory syncytial virus or adenovirus, which are more common in children.
In cases where viral pneumonia arises in conjunction with bacterial pneumonia, the use of antibiotics such as Amoxicillin, Azithromycin, Clarithromycin or Ceftriaxone is also indicated, for example, for about 7 to 10 days. Learn, too, how to identify and treat bacterial pneumonia in adults and children.
How much time does the treatment last
Generally, treatment for cases of influenza caused by influenza or pneumonia without complications, treatment is done for 5 days at home.
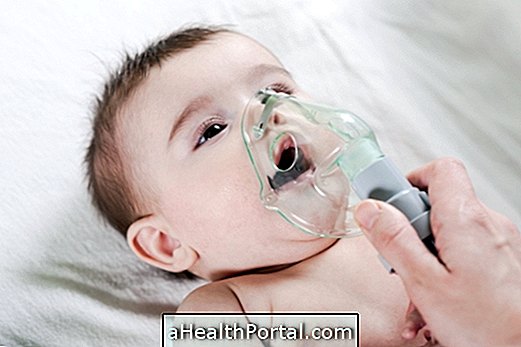
However, when the person shows signs of severity, such as difficulty in breathing, low blood oxygenation, mental confusion or changes in the functioning of the kidneys, for example, hospitalization may be necessary, with prolongation of treatment for 10 days, antibiotics in the vein and use of oxygen mask.
Care during treatment
During the treatment of viral pneumonia the patient should have some care such as:
- Avoid public places such as school, work and shopping;
- Stay at home, preferably at rest;
- Do not go to places with sudden changes of temperature, like beach or playground;
- Drink plenty of water daily to facilitate the fluidification of the cold;
- Inform the doctor if there is an increase in fever or phlegm.
Viruses that cause viral pneumonia are contagious and especially affect people with weakened immune systems. Therefore, until treatment is started, patients should wear a protective mask, which they buy at the pharmacy, and avoid direct contact through kissing or hugging, for example.
How to prevent pneumonia
To prevent this infection or prevent it from recurring, it is important to maintain good hygiene habits, such as washing hands or using alcohol gel, after using the bathroom or attending public places such as buses and malls, and avoid sharing personal objects, such as cutlery and glasses.
In addition, it is important to vaccinate against major flu types every year, free of charge at health clinics, especially those at highest risk of developing viral infections, such as children, the elderly, pregnant women, and health professionals.