Hydatidosis is a disease caused by Echinococcus granulosus and is characterized by the presence of hydatid cysts, which corresponds to the evolutionary form of the parasite that causes long-term symptoms in various arias of the body, especially the liver and lungs.
The cysts grow slowly and, when they rupture, can cause anaphylactic shock, which can result in death.
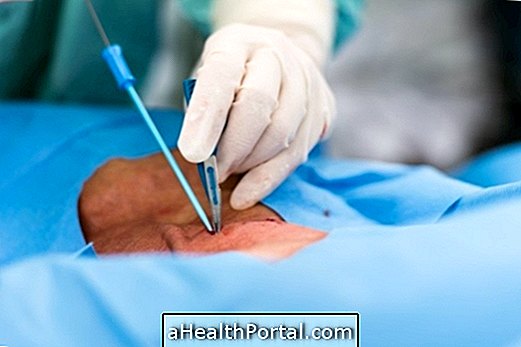
The definitive host of this parasite is the dog, being the human being an accidental host, that is infected through the ingestion of water or vegetables contaminated with the larvae of the parasite. Treatment is usually done by aspiration and elimination of the cyst, thus eliminating the parasite in the body.

Symptoms of Hydatidosis
The main sites of infection of the parasite are liver and lungs, but can also more rarely affect the brain, causing symptoms that vary by location, such as:
- Hepatic hydatidosis: is the main form of hydatidosis and is characterized by the presence of the hydatid cyst in the liver, causing symptoms such as gastric disturbance, abdominal discomfort and decreased production and release of bile;
- Pulmonary hydatidosis: is the second most frequent form of the disease and happens when the hydatid cyst develops in the lungs leading to symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue to physical exertion and cough with expectoration;
- Cerebral hyphatidosis: occurs when the parasite affects the brain, leading to neuronal changes;
- Bone hydatidosis: it is a rare form of the disease and of long duration, that is, it remains asymptomatic for several years, and can be noticed when there is a fracture, for example.
In addition to the symptoms associated with the site of development of the hydatid cyst, there may still be symptoms such as itching, fever, and allergic reactions that may progress to anaphylactic shock. Here's how to identify and treat anaphylactic shock.
The hydatid cyst develops slowing, which causes the disease to be asymptomatic for years, most of the time, making diagnosis difficult. However, the cyst can be identified can middle of routine exams such as X-ray, CT scans or ultrasounds. Thus, the diagnosis of hydatidosis is made from symptoms, imaging and laboratory tests, and the Casoni reaction is the laboratory test used to confirm the diagnosis of hydatidosis, since it identifies specific antibodies in the person's body.
Life cycle
The definitive host of Echinococcus granulosus is the dog, that is, it is in the dog that there is the development of the adult worm, whose eggs are released into the environment through the feces, contaminating food, children's hands and grasses, for example. Eggs can remain viable in the soil for several months or years and are normally consumed by the intermediate hosts, which are pigs, oxen, goats and sheep, with the development of the hydatid cyst in the liver and lungs, which can be consumed by dogs, especially in dogs. where the animals are reared for slaughter.
This disease is more frequent in children through direct contact with dogs, for example, because the eggs may be attached to the fur. In addition, contamination can occur through the consumption of contaminated food and water, allowing the eggs to enter the body, transforming into an oncosphere in the stomach, affecting the blood and lymphatic circulation, and then reaching the liver, for example. Upon reaching the liver, lung, brain or bones, the oncosphere transforms from a hydatid cyst into a slow process that can last 6 months or more.
How is the treatment done?
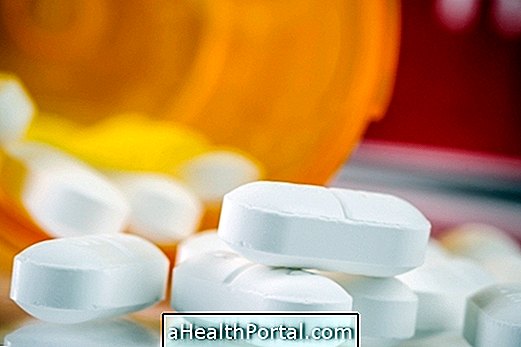
The treatment is done with the aim of eliminating the parasites from the person's body and eliminating the cysts.
The treatment is usually done with the use of medicines like Albendazole, which may be associated with Praziquantel, which can penetrate the cyst and prevent development in larva, guaranteeing the person's healing. Surgery is recommended when the cyst is very bulky and is located in an easily accessible area. The PAIR, which corresponds to Puncture, Aspiration, Infection and Breathing, is a very effective treatment method when it comes to various cysts.
Hydatidosis can lead to complications of cyst rupture, in which case the person should be admitted as soon as possible to prevent the onset of more serious complications.
How to prevent
Prevention can be done through simple measures such as:
- Medicate all dogs to decrease the likelihood of contagion;
- Basic sanitation in cities;
- Ingest only treated water;
- Wash hands after coming into contact with dogs;
- Do not handle food without washing hands;
- Always wash the kitchen utensils after being used with raw vegetables.
Also, it is important to avoid consuming raw vegetables from unknown sources, and when eating make sure they have been washed with bleach, as well as wash your hands whenever you come in contact with animals and before preparing food.