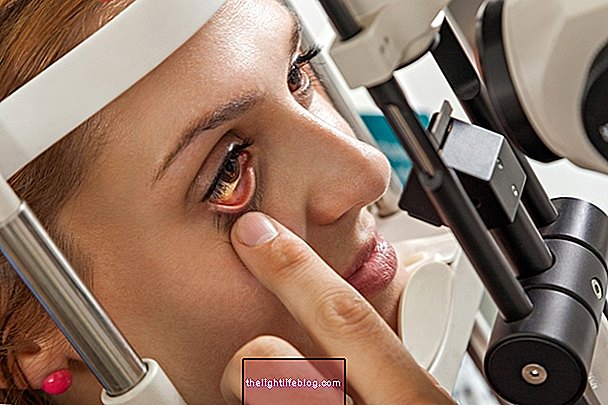
Trachoma is one of the complications caused by chlamydia, a silent STD, which gives rise to a type of chronic conjunctivitis that lasts longer than the usual 5 to 7 days.
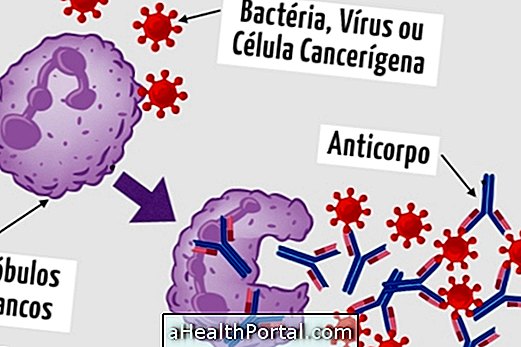
This eye infection is caused by the bacterium Chlamydia Trachomatis, which is quite contagious, especially in its early stages. The person with chlamydia in the penis or vagina can pass the bacteria to the eyes through the hands, accidentally.
Learn to recognize the symptoms of Chlamydia and how your treatment is treated.
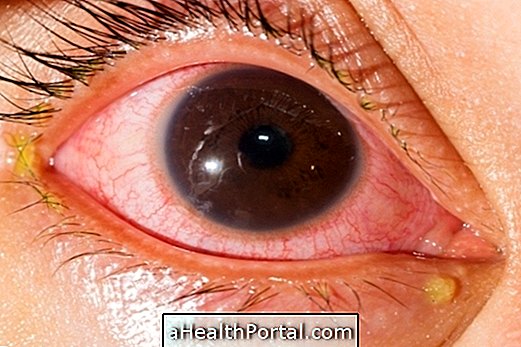
What are the symptoms
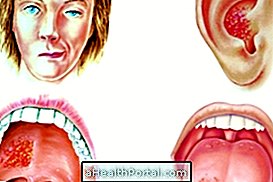
The symptoms begin to manifest between 5 to 12 days after the contact of the bacteria with the eyes and are usually:
- Red eyes,
- Swollen, pus-lidded eyelids;
- Inflammation of the eyes;
- Itchy eyes.
These symptoms are similar to a conjunctivitis, but which lasts longer with secretion, followed by scarring of the conjunctiva and cornea causing the eyelashes to go inward, which makes the disease even more painful and can injure the eyes, causing inflammation that can lead to permanent impairment of vision.
Diagnosis of trachoma can be made by the ophthalmologist through observation of the symptoms presented and is confirmed by examination of the secretion produced by the eye or scraping of the affected cornea.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment involves the application of antibiotic ointments for 4 to 6 weeks, or even the taking of oral antibiotics such as doxycycline, which is also used in the treatment of other infections by the same bacterium Chlamydia Trachomatis .
Passing sterile compresses into the eyes soaked in saline is a more pleasant way to keep the eyes clean and free of bacteria, and then discard those that are used.
To treat the consequence of recurrent infections, which is the inversion of the eyelashes into the eyes, one may resort to surgery, which corrects by reversing the birth direction of the eyelashes up and out of the eye again. Another alternative to solve the problem is the use of the laser that burns the root of the hair preventing new growth.
How is prevention done?
Trachoma is an infection caused by bacteria, so maintaining hygiene is the most effective strategy for the prevention of trachoma. It is therefore recommended to always keep your hands and eyes clean with clean water and soap and do not carry your eyes even if they appear to be washed because you can not see the microorganisms with the naked eye.