This is a chronic disease characterized by a decrease in insulin production and / or resistance to its action. The two most common types are type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes, but there are also insipidus and gestational types.
The diagnosis is determined when a common blood test confirms that insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas that should carry sugar into cells to be used as a source of energy, is not produced or used by the body properly, blood sugar.
This disease affects both men and women of any race, although it is even more common in more mature or elderly individuals.
Symptoms of diabetes
The characteristic symptoms are:
- Very thirst;
- Increased urge to urinate;
- Slimming, although not dieting and eating the same way;
- Very hungry;
- Poor healing;
- Tiredness and
- Poor circulation.
Learn to recognize early symptoms in children, adolescents, and adults.
Decompensation causes not only increased blood sugar, but also disorders in the metabolism of fats and proteins. The complications may be diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar syndrome and hyper or hypoglycemia.
Diabetes screening exam
The test that determines whether an individual is diabetic or not is the examination of the glycemic curve, performed fasting and also after the ingestion of an extremely sweet substance. In this case, the reference values after 2 hours are:
- Normal: less than 140 mg / dl;
- Tolerance decreased to glucose: between 140 and 199 mg / dl;
- Diabetes: equal to or greater than 200 mg / dl.
The individual is considered pre-diabetic when the values of this test are between 140 and 199 ml / dl and should be given the same care for diabetics, such as avoiding not eating for more than 4 hours and not eating sweets or carbohydrates, since these can easily develop the diabetic picture. If you follow the recommendations you may not develop the disease.
Diabetes can also develop in pregnancy, but it does not always affect the fetus and tends to disappear in the postpartum period. But when complications arise, the baby may develop a picture of hypoglycemia soon after birth and is at greater risk of suffering from the disease in adult life. When a woman is diabetic and then decides to become pregnant, it is recommended that she have her blood glucose checked for at least 6 months before attempting to conceive to reduce her chances of suffering from malformation.
Treatment
Treatment for type 1 diabetes, in which the individual has not been producing insulin since childhood or from adolescence, is based on insulin administration and blood glucose control. In the case of type 2 diabetes, a well-balanced and balanced diet is often sufficient to maintain blood glucose and control the progression of the disease.
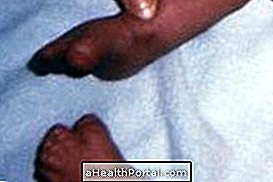
This disease has no cure and should be controlled daily to avoid more serious complications such as vision problems, diabetic foot or infertility for example. The practice of regular exercise and moderate intensity is strongly recommended to keep the diabetic compensated.
See too:
- Symptoms of diabetes
- Types of diabetes
- Carbohydrate counting for diabetics