Which is:
Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas that is responsible for carrying the glucose that is in the blood into the cells to be used as a source of energy, fat in the cells and protein in the muscles.
The main stimulus for insulin production is the increase in blood glucose after meals. When the production of this hormone is insufficient or absent, as in diabetes, sugar accumulates in the blood and urine, causing complications such as retinopathy, renal failure, injuries that do not heal and stroke, for example.
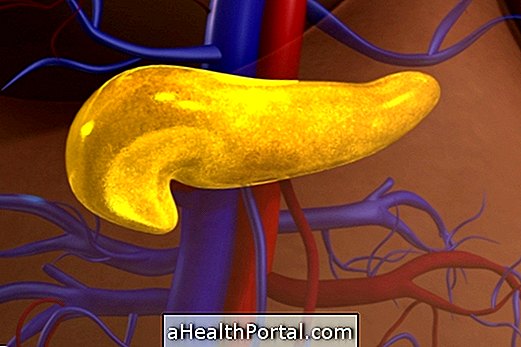
Diabetes is the disease that changes the amount of insulin produced because it affects the ability of the pancreas to produce this hormone, either from birth, which is type 1 diabetes, or be acquired throughout life, which is type 2 diabetes, and in these cases it may be necessary to use drugs to control sugar levels or even use synthetic insulin to mimic the action of what is produced in the body.
How Insulin Works
Insulin has the ability to pick up glucose from the blood, and carry it to the body's organs, such as brain, liver, fat and muscles, where it can be used to produce energy, proteins, cholesterol and triglycerides to give energy to the body. body, or to be stored.
The pancreas produces insulin in 2 ways:
- Basal : which is the continuous secretion of insulin, to maintain a constant minimum throughout the day;
- Bolus : is when the pancreas releases large amounts at a time, after each feeding, thus preventing the sugar from food from accumulating in the blood.
There is another hormone, also produced in the pancreas, which has counter-acting insulin, called glucagon. It works by releasing the glucose that is stored in fat, liver and muscle to the blood so that the body uses it when sugar levels are very low, such as when we are fasting, for example.
The action of these 2 hormones, insulin and glucagon, is very important to balance the amount of glucose in the blood, preventing it from getting too much, causing the complications of diabetes, such as heart attack, stroke, vision loss and injuries, or missing, which causes loss of energy and strength, as both situations bring bad complications to the body. Understand better about symptoms and how to identify diabetes.

When to take insulin
It is necessary to replenish insulin through medications with the synthetic hormone in situations where the body can not produce it in the required amounts, such as in type 1 diabetes or severe type 2 diabetes. Understand better when it is necessary for the diabetic to start insulin.
The insulin of the drugs mimics the body's insulin secretion throughout the day, both basal and bolus, so there are several types, which differ by how fast they act on blood glucose:
Basal action insulin
They are synthetic insulins that mimic the basal insulin that is released gradually by the pancreas, and can be:
- Intermediate Action or NPH, such as Insulatard, Humulin N, Novolin N or Insuman Basal: has a duration of up to 12 hours in the body, also can be used to maintain a constant amount of insulin in the body;
- Slow action such as Lantus, Levemir or Tresiba: is the insulin that is released continuously and slowly over 24 hours, which maintains a minimal action throughout the day.
Ultra-deep-acting insulins with a duration of up to 42 hours are also being marketed, which can give greater comfort to the person, reducing the number of bites.
Bolus Action Insulin
They are the hormones used to replace the insulin that is produced after eating, to prevent glucose from rising too fast in the blood, and are:
- Fast or Regular Insulin, such as Novolin R or Humulin R: mimics the insulin that is released when we eat, so it starts its action in 30 minutes, taking effect for about 2 hours;
- Ultra-fast insulin, such as Humalog, Novorapid and Apidra, is the insulin that has an almost immediate action to prevent food from increasing blood sugar levels too much and should be applied just before eating.
These substances are applied to the fat tissue under the skin with the help of a syringe or special pens for this function. In addition, one option is to use the insulin pump, which is a small device that stays attached to the body, and can be programmed for the release of basal or bolus insulin according to the need of each person.
Learn more about insulin types, their properties and how to use them.