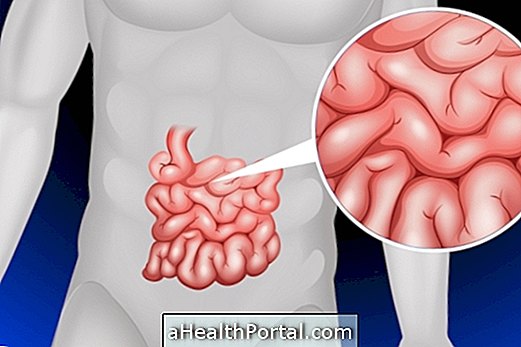
The polyp sessil is a type of polyp that usually develops in the intestine and has a broader base than normal. Polyps are produced by the abnormal growth of tissue in the wall of an organ, such as the intestines, stomach or uterus, but may also arise in the ear or throat, for example.
Although they may be an early sign of cancer, polyps do not always have a negative prognosis and can often be removed without any change to the person's health.

When the polyp can be cancer
Polyps are almost always considered an early sign of cancer, however, this is not always true, as there are several types of sessile polyp, according to their characteristics and risk of turning cancer:
- Sesil adenoma sessil : presents a saw-like appearance, is considered a pre-cancerous type and, therefore, must be removed;
- Viral adenoma : is at high risk of being cancer and usually arises in cases of colon cancer;
- Tubular adenoma : is the most common type of polyp and usually has a very low risk of being cancer;
- Tubulo-villous adenoma : they have a growth pattern similar to tubular adenoma and villous and, therefore, their degree of malignancy may vary.
Since most polyps are at some risk of becoming cancer, even if low, they should be completely removed after being diagnosed, to prevent them from continuing to grow and to develop some form of cancer.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment of polyps is almost always done during the diagnosis. Because it is most common for polyps to appear in the gut or stomach, the doctor usually uses the endoscopy or colonoscopy to remove the polyp from the wall of the organ.
However, if the polyp is too large, surgery may be needed to completely remove the polyp.
During removal, a cut is made in the wall of the organ and, therefore, there is a risk of bleeding. For this reason it is important to perform colonoscopy and endoscopy exams at accredited clinics to ensure that doctors can stop bleeding.
Understand better how endoscopy and colonoscopy are done.
Who has a higher risk of having a polyp
The causes of the polyp are still not known, especially when it is not produced by a cancer, however, there seem to be some factors that increase the risk of developing, such as:
- Being obese;
- Eat a diet high in fat and low in fiber;
- Consume red meat in lots;
- Be over 50 years old;
- Have a family history of polyps;
- Use cigarettes or alcohol;
In addition, people who have chipercaloric diets and who do not exercise often, also appear to have a greater risk of developing a polyp.