Scoliosis is a lateral curvature of the spine, which leaves it in the form of an 'S'. Although their development in adolescents is more common, children may also be affected, especially when other changes such as cerebral palsy are present, for example.
However, most often, scoliosis is idiopathic, which means that its exact cause can not be identified. It is related to a number of factors such as lack of physical activity, poor posture and long sitting or lying down with the spine.
Another factor that can lead to scoliosis is one leg being shorter than the other because a difference in leg size greater than 2 cm may tilt the hip and this will change the position of the spine and in that case the treatment should be done with the correction of the size of the legs as well.
How to identify
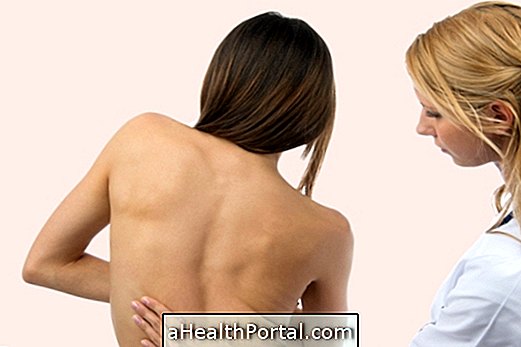
It is possible to suspect a scoliosis in the spine when the person has one shoulder higher than the other, or shoulder blades that are the bones of the back that are also popularly called 'wings' are tilted or when one side of the hip tilted up.
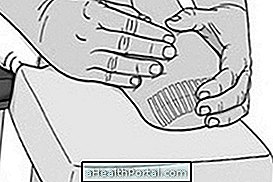
The orthopedist or physiotherapist can ask the person to have a test to identify scoliosis, or the need for tests. The scoliosis test consists of:
Stand with your legs hip-width apart and lean your body forward to touch with your hands on the floor, keeping your legs straight. If you can not get your hands on the floor, you do not have to force yourself. In this position the professional can observe if a higher region of the column of one of the sides appears. If it is possible to observe this 'high' it indicates that there is a scoliosis of this same side.
However, it is possible that the test does not show scoliosis, and this can only be seen in the examination. In this case, scoliosis is only postural and exercises and physiotherapy are the most suitable for treatment.
In addition, your doctor may order a X-ray examination to look at the position of the spine. This exam should show the vertebrae of the spine and also the hip. The first image is the performance of the test and the second one shows an X-ray of the column with scoliosis:


The diagnosis of scoliosis can be done without imaging tests, but these are important to indicate also the degree of inclination that the person has, which is important to decide the treatment. See how the X-ray exam works.
Types of scoliosis
Scoliosis can be classified according to its causes or with the twisting region of the spine. According to the cause of scoliosis, it can be:
- Idiopathic, when the cause is unknown, and can be classified as infantile, when it appears until the age of 3 years, juvenile, when it appears between 3 and 9 years, and adolescent, when it happens between the 10 and 18 years;
- Congenital, in which the baby is already born with scoliosis due to the malformation of the vertebrae;
- Degenerative, which arises in adulthood due to injuries, such as fractures and osteoporosis, for example;
- Neuromuscular, which happens as a consequence of neurological conditions, such as cerebral palsy, for example.
In relation to the torsion region of the spine, scoliosis can be classified as cervico-thoracic, thoracic, thoracolumbar, lumbar and lumbosacral. In the case of lumbar scoliosis, the twisting of the spine occurs in the lumbar region, and the curvature may be to the left or right.
How to treat
Treatment for scoliosis can be done with physical therapy, vest wear, or spine surgery. Learn more about scoliosis treatment.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy is indicated to treat scoliosis up to 35 degrees of curvature and can be done through therapeutic exercises, Clinical Pilates exercises, spinal manipulation techniques, osteopathy and corrective exercises such as the postural reeducation method. Understand what the method of postural reeducation is.
Vest
When the person has between 20 and 35 degrees of curvature, in addition to physical therapy it is also recommended to wear a special vest called Charleston that should be worn at night during sleep, and the Boston vest, which is to be worn during the day to study, work and do all the activities, and should be withdrawn only for the bath. The vest should be recommended by the orthopaedist and to have the expected effect should be used as long as possible.
Surgery
When the column has more than 36 degrees of curvature, surgery is indicated to reposition the vertebrae of the spine on the central axis. Usually the surgery is indicated for children or adolescents, that is when the results are better and the treatment more effective. Surgery can be done to place plates or screws to center the spine.