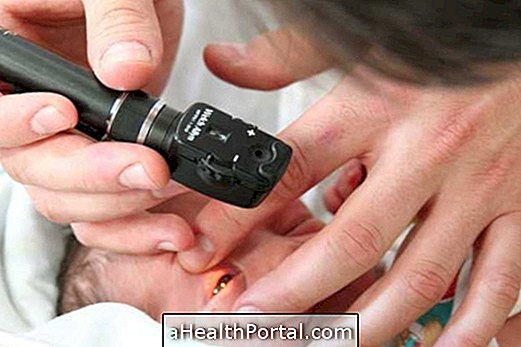
The Wood lamp, also called Wood or LW light, is a diagnostic device widely used in dermatology and aesthetics in order to verify the presence of skin lesions and their extension characteristics according to the fluorescence observed when the lesion is exposed to low wavelength UV light.
Wood's light lesion analysis should be done in a dark environment and with no visible light to make the diagnosis as accurate as possible, so that the dermatologist can indicate the best treatment option.

What is it for
The Wood lamp is used to determine the degree and extent of the dermatological lesion, aiding the diagnosis and definition of the treatment. Thus, LW can be used to:
- Differential diagnosis of infectious dermatoses, which may be caused by fungi or bacteria;
- Hypo- or hyperchromic lesions with vitiligo and melasma, for example;
- Porphyria, a disease characterized by the accumulation of substances in the body that are precursors of porphyrin, which can be detected in the urine, in addition to the evaluation of skin lesions;
- Presence of oiliness or dryness of the skin, and LW can be used before aesthetic procedures, as it allows the professional to check the characteristics of the skin and determine the most appropriate cosmetic procedure for that type of skin.
According to the luminescence color, it is possible to identify and differentiate the dermatological lesions. In the case of infectious dermatoses, fluorescence represents the infectious agent, but in the case of porphyria, the fluorescence happens as a function of the substances present in the urine.
In the case of pigmentation disorders, Wood's lamp is used not only to evaluate the limits and characteristics of the lesion, but also to verify the presence of subclinical lesions that were not identified in the conventional dermatological examination, only by fluorescence.
Although the use of Wood's lamp is very effective in the diagnosis and monitoring of the evolution of the lesions, its use does not exempt the conventional dermatological examination. Understand how the dermatological examination is done.
How it works
The Wood lamp is a small and inexpensive device that allows to identify various dermatological lesions according to the fluorescence pattern observed when the lesion is illuminated at a low wavelength. UV light is emitted at a wavelength of 340 to 450 nm by an arc of mercury and is filtered through a glass plate composed of barium silicate and 9% nickel oxide.
For the diagnosis to be the most correct, it is necessary that the evaluation of the Wood lamp lesion is done 15 cm from the lesion, in a dark environment and without visible light, so that only the fluorescence of the lesion is perceived. The fluorescence pattern of the most frequent dermatological lesions are:
| Disease | Fluorescence |
| Tinea | Blue-green or light blue, depending on the species causing the disease; |
| Pityriasis versicolor | Yellow-silver |
| Erythrasma | Red orange |
| Acne | Green or reddish orange |
| Vitiligo | Bright blue |
| Melasma | Dark brown |
| Tuberous sclerosis | White |
| Porphyria | Red-orange urine |